Figure 3.
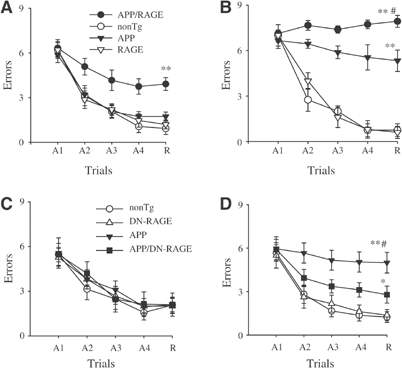
Functional neuronal deficits: spatial learning and memory in Tg mAPP/RAGE and Tg mAPP/DN-RAGE mice. (A, B) Spatial learning and memory was tested in the radial arm water maze at 3–4 (A) and 5–6 months of age (B) in mice of the indicated genotypes (in (A), n=7–8 male mice/genotype; in (B), n=5 male mice/genotype): Tg mAPP/RAGE (APP/RAGE), nonTg littermate (nonTg), Tg mAPP (APP), and Tg RAGE (RAGE). (A1–A4) denote the acquisition trials, and R denotes the retention trial. In panel A, **P<0.01 Tg mAPP/RAGE compared with nonTg mice (by repeated-measure ANOVA followed by Fisher's protected least significant difference for post hoc comparisons in this and the following graphs). In panel B, **P<0.01 Tg mAPP/RAGE and Tg mAPP mice compared with nonTg mice; #P<0.01 Tg mAPP/RAGE compared with Tg mAPP mice. ANOVA revealed a main age effect in Tg mAPP/RAGE mice and Tg mAPP mice (P<0.05 for both), but not in nonTg and DN-RAGE mice (P>0.05 for both). (C, D) Effect of DN-RAGE transgene on spatial learning and memory in Tg mice at 3–4 months (n=5–8 male mice/genotype (C)) and 5–6 months (n=6–9 male mice/genotype (D)). The following genotypes were tested: nonTg littermate (nonTg), Tg DN-RAGE (DN-RAGE), Tg mAPP (APP), and Tg mAPP/DN-RAGE (APP/DN-RAGE). In panel D, **P<0.01 Tg mAPP mice compared with nonTg mice; #P<0.01 Tg mAPP mice compared with Tg mAPP/DN-RAGE mice, and *P<0.05 Tg mAPP/DN-RAGE mice compared with nonTg littermates. ANOVA revealed a main age effect in Tg mAPP mice (P<0.05) but not in Tg mAPP/DN-RAGE, DN-RAGE, and nonTg mice (P>0.05).
