Figure 5.
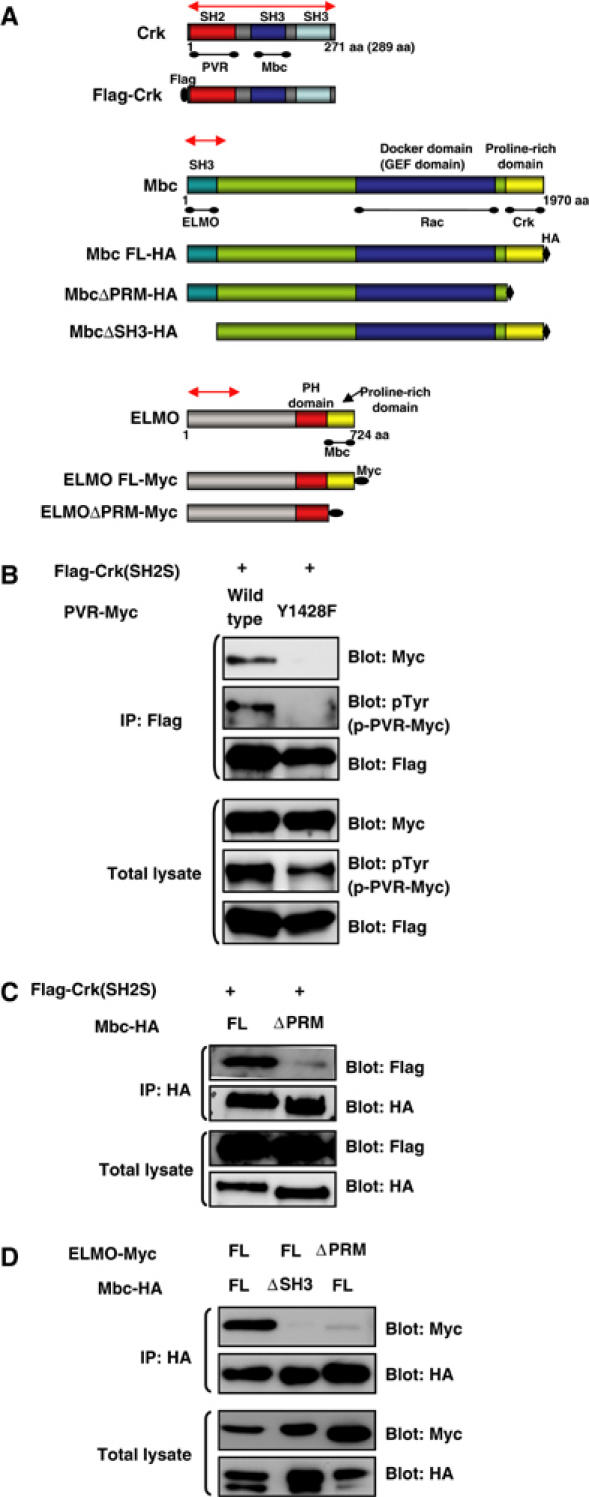
Physiological interactions among PVR, Crk, Mbc, and ELMO. (A) Schematic diagram of WT and modified forms of Crk, Mbc, and ELMO constructs used in this study. For the biochemical interaction experiments, Crk, Mbc, and ELMO were Flag, HA, and 6X Myc tagged, respectively. A corresponding region (approximately 700 bp in length) of each gene was used as a template for in vitro synthesis of dsRNA and for the IR construct, indicated by a red line with double arrowheads. PRM: proline-rich motif, FL: full length. (B) The C-terminal tyrosine phosphorylation site of PVR (Y1428VTP in Figure 1A) is required for interaction with Crk (SH2S). S2 cells were transfected with Myc-tagged WT or Y1428F mutant constructs of PVR cloned in the pUAST vector together with pUAST Flag-Crk (SH2S) and pWAGAL4, the latter of which supplied the GAL4 protein. After 48 h, the cells were lysed, immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag (rabbit polyclonal) antibody, and immunoblotted with anti-Myc, anti-pTyr, or anti-Flag (mouse monoclonal) antibodies. The total lysates from the same experiment were immunoblotted with the same antibodies to see the expression of PVR and Crk and the tyrosine phosphorylation level of PVR molecules. (C) C-terminal region of Mbc is required for interaction with Crk. S2 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids coding for Flag-Crk (SH2S) along with Mbc-HA (lane 1) or Mbc ΔPRM-HA (lane 2). The lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody and immunoblotted with anti-Flag antibody. The same blot was then stripped and reprobed with anti-HA. Immunoblotting of total lysates indicated the expression of HA-tagged Mbc molecules and Flag-Crk. (D) ELMO interacts with the SH3 domain of Mbc through its C-terminal PRM. S2 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids coding for HA-tagged Mbc FL or Mbc ΔSH3 along with 6X Myc-tagged ELMO FL or ELMO ΔPRM. After anti-HA immunoprecipitation, the co-precipitation of Myc-tagged ELMO molecules was analyzed by anti-Myc immunoblotting. The same blot was then stripped and reprobed with anti-HA. Immunoblotting of total lysates indicated the expression of HA-tagged Mbc and Myc-tagged ELMO molecules.
