Figure 1.
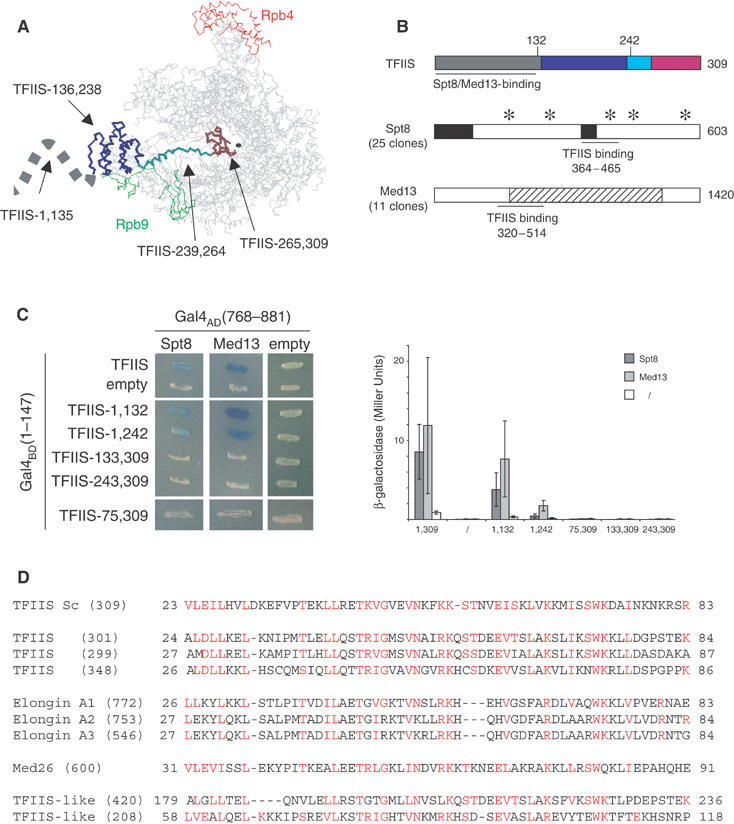
Spt8 and Med13 are TFIIS partners in a two-hybrid assay. (A) Spatial structure of the RNA polymerase II–TFIIS complex domain I, domain II, the inter-domain linker and domain III of TFIIS are shown in grey, blue, cyan and brown, respectively. The borders of each domain are taken from the crystal structure recently reported by Kettenberger et al (2003). The structure of the N-terminal domain I (positions 1–111, symbolised here by a dashed line) was solved in solution by nuclear magnetic resonance (Booth et al, 2000), but was not determined in association with Pol II. The Rpb4 and Rpb9 subunits of Pol II are indicated in red and green, respectively. The black sphere locates the catalytic Mg2+ A. This figure was prepared with the RASMOL software (www.umass.edu/microbio/rasmol/). (B) General organisation of Spt8, Med13 and TFIIS. TFIIS: The TFIIS domains are shown in the same code colour as in (A). A horizontal thick line denotes the minimal region supporting a two-hybrid interaction with Spt8 and Med13, based on the data shown in (C). Spt8: Stars and black boxes indicate WD40-like domains and acidic stretches, respectively. The horizontal thick line denotes the TFIIS-binding region (positions 364–465) as defined by the smallest domain common to the 25 pACT2-SPT8 clones identified by a two-hybrid screening using pVV70 as bait vector (Table II). An example of two-hybrid interaction is shown in (C). Med13: The stripped box corresponds to a region with strong homology between fungal forms of Med13. The horizontal thick line denotes the TFIIS-binding region (positions 320–514), as defined by the smallest domain common to the 11 pACT2-MED13 clones selected by two-hybrid screening. An example of two-hybrid interaction is shown in (C). (C) Two-hybrid interactions with TFIIS. Left panel: The complete coding sequence of TFIIS and various N-terminal or C-terminal fragments thereof were fused to the C-end of the GAL4BD(1–147) DNA-binding domain (plasmids pVV70–pVV75, Table II) and tested for their interaction with Spt8 (plasmid pSPT8-84) and Med13 (plasmid pMED13-111). Transformants were obtained in strain Y190 and tested at 30°C for β-galactosidase activity in an overlay assay (Flores et al, 1999). Right panel: β-Galactosidase activity was assayed as described by Miller (1972). The average values and their standard deviation were calculated from assays performed on three independent transformants, using the same plasmid combination as in the left panel. (D) Conservation of the TFIIS N-terminal domain. The S. cerevisiae (Sc) sequence of TFIIS was compared to the current human genome. Homology search was made using the Psi-blast algorithm and improved by manual inspection. The number in brackets indicates the length of each polypeptide. The two last sequences (accession number AAH35374 and XP294568) correspond to putative gene products that are related to TFIIS but lack the invariant RSADE motif.
