Figure 6.
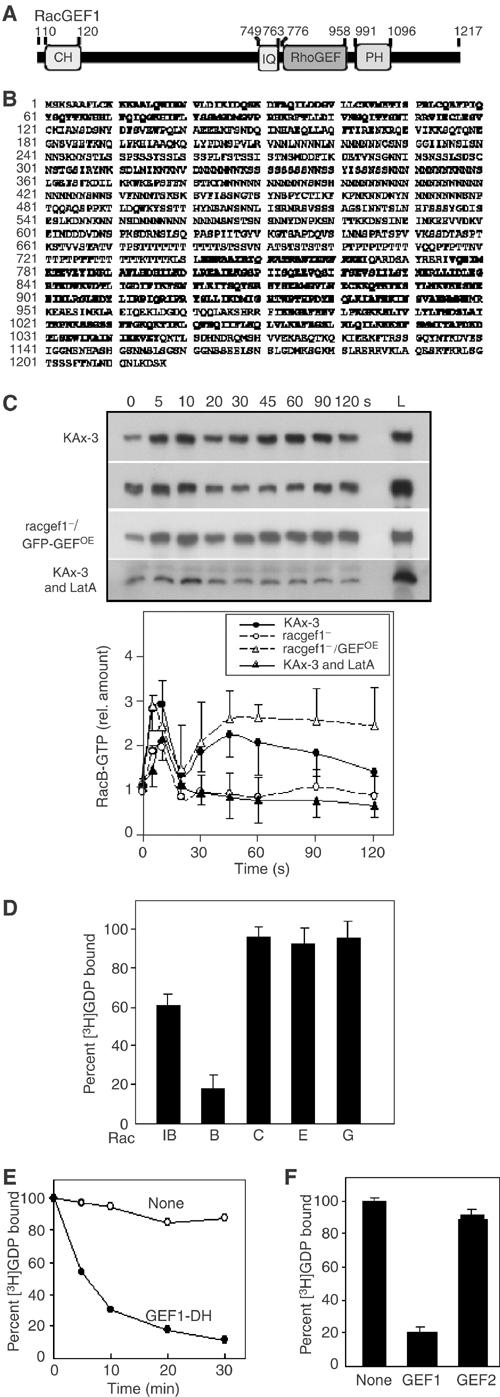
RacGEF structure and function. (A, B) Domain structure and derived amino-acid sequence of RacGEF1. The CH, IQ, RhoGEF (or DH), and PH domains are in bold face. (C) RacB-GTP in the stimulated wild-type cells, racgef1 null and overexpressing cells, and wild-type cells treated with LatA (upper panel). Lane L indicates the levels of total myc-RacB in the same volume of each lysate. RacB-GTP levels were determined by densitometry of developed Western blot films in at least three independent experiments (lower panel). (D) Comparison of RhoGEF domain abilities of RacGEF1 to catalyze GDP/GTP guanine nucleotide exchange on Rac1B, RacB, RacC, RacE, and RacG. (E) Time course of RhoGEF domain activity of RacGEF1 to catalyze GDP/GTP guanine nucleotide exchange on RacB. (F) Comparison of RhoGEF domain abilities of RacGEF1 and RacGEF2 to catalyze GDP/GTP guanine nucleotide exchange on RacB.
