Figure 2.
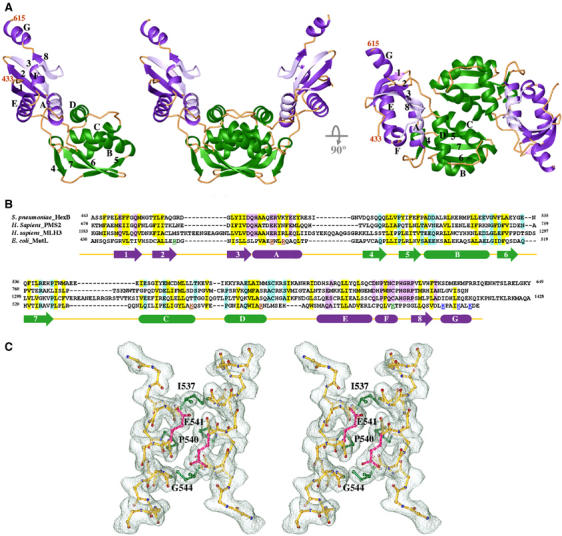
Crystal structure of LC20. (A) Ribbon diagrams of one LC20 subunit and two orthogonal views of an LC20 dimer. The Ex and In subdomains are shown in purple and green, respectively. Secondary structures are labeled in one subunit. (B) Sequence alignment of the C-terminal dimerization domains of Streptococcus pneumoniae HexB, human PMS2 and MLH3, and E. coli MutL. Secondary structures of LC20 that are predicted to also exist in the other three proteins are shown as arrows (β-strand) and boxes (α-helices). Conserved hydrophobic and polar residues are highlighted in yellow and purple (Ex) or green (In). Residues mutated in P-1, P-2 and P-3 are color coded in red, blue and green, respectively. (C) Stereo view of the pair of αC helices at the dimer interface. A 2Fo−Fc electron density map is superimposed. Side chains of Ile537, Pro540 and the Cα atom of Gly544 are highlighted in green, and side chains of Glu541 in pink. Other side chains of the αC helix are omitted for clarity. Figures 2A, C and 3 were generated using RIBBONS (Carson, 1987).
