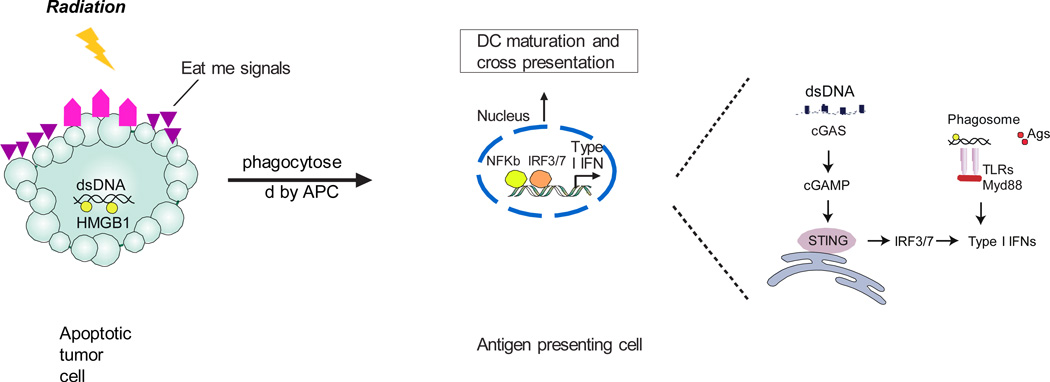
Figure 1. Irradiation mediated sensing of tumor-derived DNA for induction of type I interferons (IFNs) in antigen-presenting cells (APCs).
Radiation results in the release of “find-me” and “eat-me” signals from tumor cells. During phagocytosis in myeloid cells, the DNA fragments hidden in irradiated tumor cells are released from phagosomes to cytoplasm, acting as a danger signal. The cGAS binds this DNA and generates cGAMP as a second messenger. cGAMP binds to STING, which subsequently activates IFN regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) or IRF7 to induce type I IFN production. Alternatively, DNA released from dying tumor cells can theoretically activate endosomal TLR9 and induce type I IFN production through Myd88.