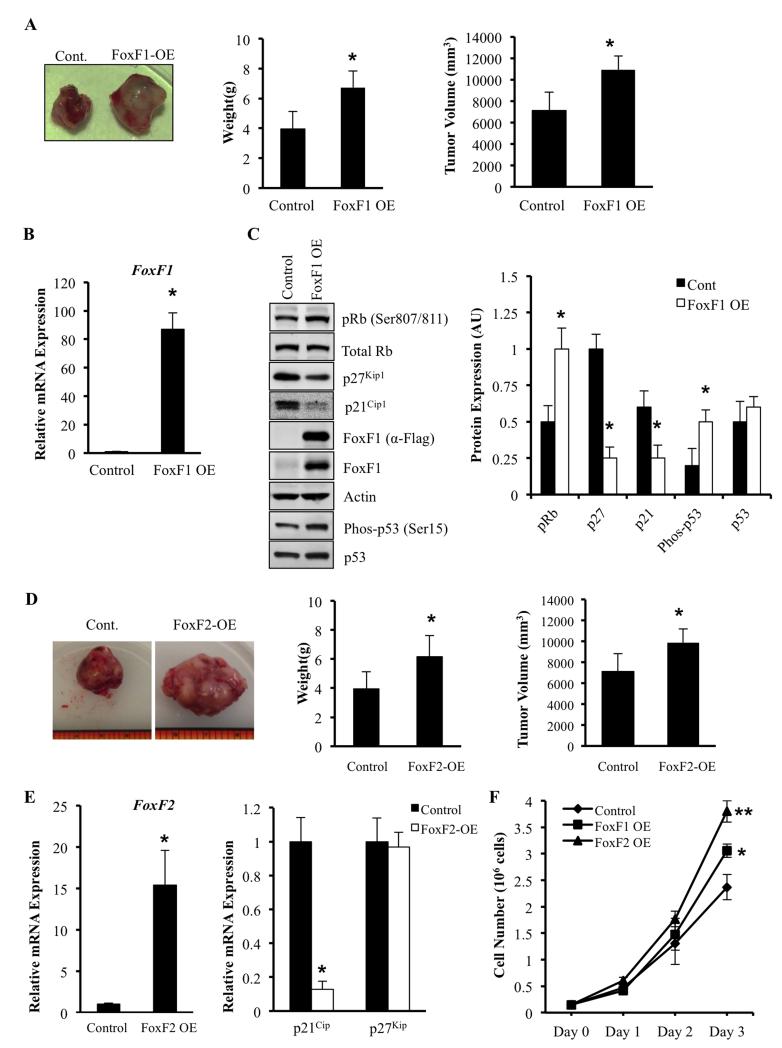
Figure 6. Overexpression of FoxF1 or FoxF2 promotes tumor growth by decreasing expression of p21Cip1 and p27Kip1.
(A) Representative tumors formed 3 weeks after receiving intra-muscular injection of 2 ×105 76-9 cells transduced with an empty-vector control or FoxF1 overexpression retrovirus (FoxF1-OE). Tumor weights and volumes for mice (n=5) are shown as mean ± SD. (B) Efficiency of FoxF1 overexpression was confirmed by qRT-PCR using total RNA isolated from orthotopic RMS tumors. FoxF1 expression levels were normalized to β-actin mRNA. (C) Overexpression of FoxF1 decreased protein levels of pRb, p21Cip1 and p27Kip1 shown by Western blot using of total protein from RMS tumors. Blots were probed with antibodies against phosphorylated Rb (pRb), total Rb, p21CIP1, p27Waf1/Cip1, Flag, FoxF1, p53, phospho-p53, or β-actin (left panel). Relative expression levels of these proteins were determined with densitometry and normalized to β-actin (right panel). AU=arbitrary units. (D) Representative tumors formed 3 weeks after receiving intra-muscular injection of 2 ×105 76-9 cells transduced with an empty-vector control or FoxF2 overexpression retrovirus (FoxF1-OE). Tumor weights and volumes for mice (n=7) are shown as mean ± SD. (E) Efficiency of FoxF1 overexpression was confirmed by qRT-PCR using total RNA isolated from orthotopic RMS tumors (left panel). Overexpression of FoxF2 increased p21Cip1 mRNA as shown by qRT-PCR using total RNA isolated from rhabdomyosarcoma tumors (right panel). β-actin mRNA was used for normalization. All data represent mean ± SD of three independent determinations using tumor tissue from n=5–7 mice in each group. (F) Overexpression of FoxF1 or FoxF2 increased proliferation of RMS tumor cells in vitro. 76-9 control, FoxF1 OE, or FoxF2 OE cells were plated in triplicates. Cell numbers were measured every 24 hours for 3 days. Each point represents mean±SEM. Data represent mean±s.d. of three independent experiments. A p value <0.05 is shown with (*), a p value <0.01 is shown with (**).