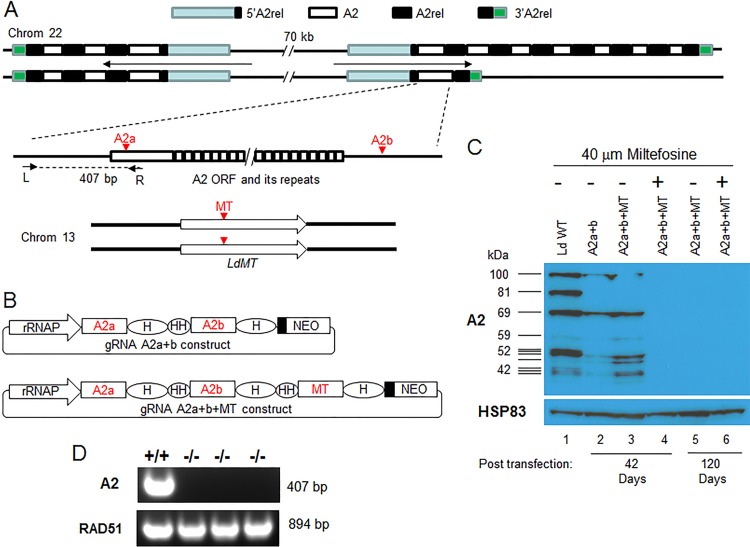
FIG 2 .
Deletion of the multicopy A2 family genes and increased efficiency through coselection for parasites with CRISPR-Cas9 activity. (A) Schematic drawing of A2-A2rel gene cluster loci in L. donovani 1SCl2D chromosome 22 and the A2 deletion coselection strategy through cotargeting the LdMT (miltefosine transporter gene). There are two nonidentical A2-A2rel gene clusters with outward transcription directions in chromosome 22. The 1SCl2D strain has at least 11 copies of A2 genes of various sizes, which alternate with A2rel genes and are flanked by 5′ A2rel and 3′ A2rel genes. The A2 and MT gRNA-targeting sites and primers used to verify A2 gene deletion are indicated. Note that this putative A2-A2rel gene cluster is based on our previous A2-targeting study (8) plus recent unpublished PacBio genome sequencing data. Because of multicopies and repeated sequences, the A2-A2rel gene cluster loci are not properly assembled in published L. donovani and L. infantum genomes (TriTrypDB). (B) The double- and triple-gRNA expression vectors used to target A2 and LdMT genes. rRNAP, L. donovani rRNA promoter; H, HDV ribozyme; HH, Hammerhead ribozyme. Black boxes represent the 92-bp pyrimidine track. The drawing is not to scale. (C) Western blot analysis of A2 proteins in L. donovani transfected with the double- or triple-gRNA expression vectors (as in panel B), with or without miltefosine selection. Equal loading of cell lysates was verified by reprobing the membrane with anti-HSP83 antibodies. (D) PCR verification of A2 null mutants using A2-specific primers L and R. The genomic DNA quality for each sample was verified by PCR with RAD51-specific primers.