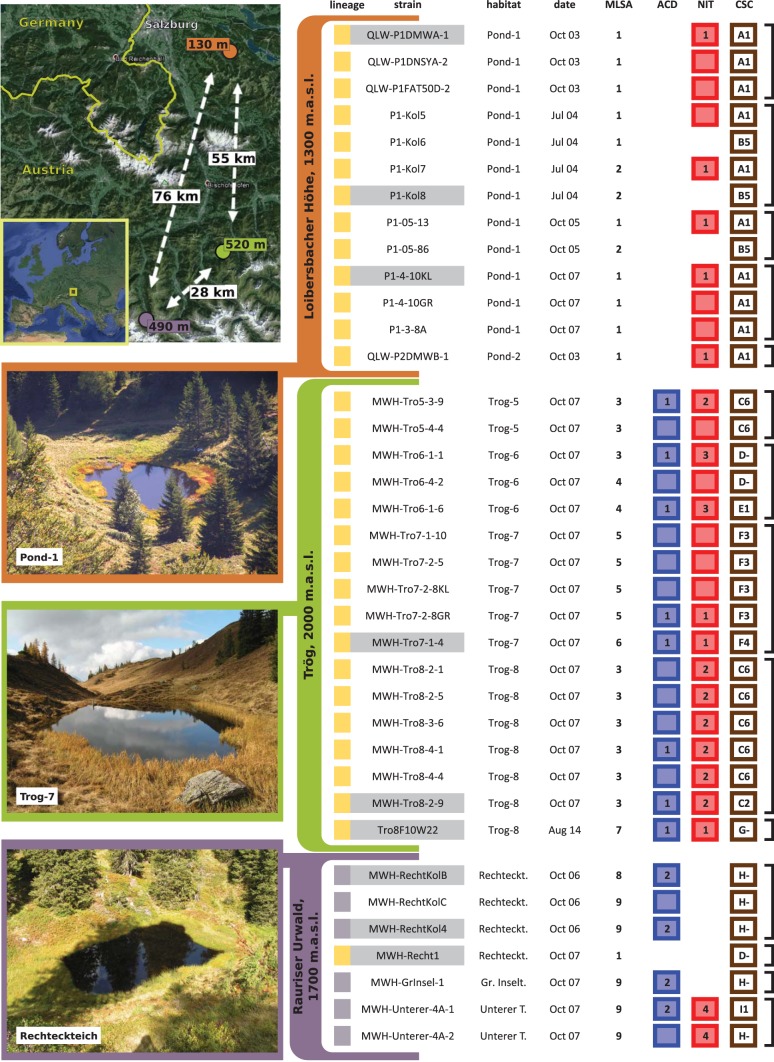
FIG 1.
Isolated P. asymbioticus strains and their diversity regarding MLSA and three GI variants. Upper left, maps depicting geographic locations of the sites of origin of the 37 cultivated P. asymbioticus strains. Air line distances between the sites are given in kilometers, and maximum distances between the habitats within the sites are given in meters. Satellite pictures were adopted from Google Earth. Bottom left, the three sites, with a photo of one habitat from each site. Right table, characterization of the 37 strains sorted by site of origin (color code), habitat of origin, sampling date, and MLSA sequence type. The left boxes are colored according to lineage affiliation (yellow for simplex, and blue for amplus), while boxes on the right represent the GI variants ACD, NIT, and CSC, respectively. The GI variant CSC is characterized for each strain concerning presence/absence patterns of selected genes (A to I) and sequence types of one gene present in 27 strains (1 to 6, and − for strains lacking the gene). For each strain, the presence of the GI variant ACD (catechol 1,2-dioxygenase gene [catA]) is indicated by a cyan box. The presence of NIT (assimilatory nitrate reductase catalytic subunit gene [nasA]) is displayed by red boxes. Sequence types of the genes are given by numbers in the boxes. In cases where no number is shown, the respective gene was not subjected to DNA sequencing. The black brackets on the right enclose strains obtained from single samples.