FIG 5.
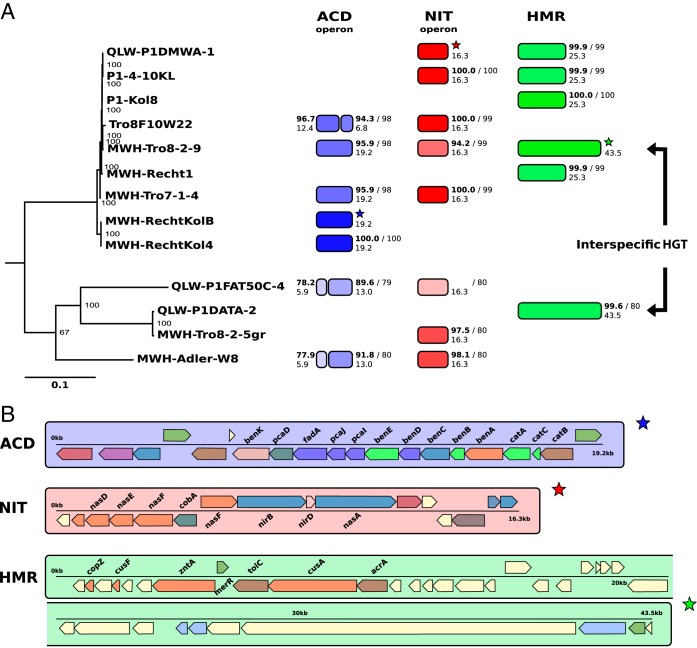
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) of GIs. (A) A phylogenetic tree (RAxML) based on 344 conserved genes among the nine genome-sequenced P. asymbioticus strains and four genome-sequenced Polynucleobacter strains not affiliated to the same species is shown on the left. The tree is rooted on Polynucleobacter rarus strain MT-CBb6A5, which is not shown in the tree. Numbers at the nodes display bootstrap support from 100 rapid bootstrap inferences. Next to the strains, the presence of three different DNA fragments corresponding to three GI variants (ACD, NIT, and HMR) is indicated by colored segments. Homologies are illustrated with respect to reference fragments indicated by stars. Sequence similarities are represented by the transparencies of the colors and written on the top next to the segments in small boldface numbers (%). Alignment lengths to the reference fragments are represented by lengths of the segments and written below the similarity values (in kilobase pairs). ANI values between the respective genomes and the reference genomes are written next to the similarity values after the slash. (B) The three reference DNA fragments from panel A are shown in detail. Genes are colored according to COG categories. The gene symbols of those genes associated with the presumed functions of the three GI variants are written above or below the genes.