FIG 3.
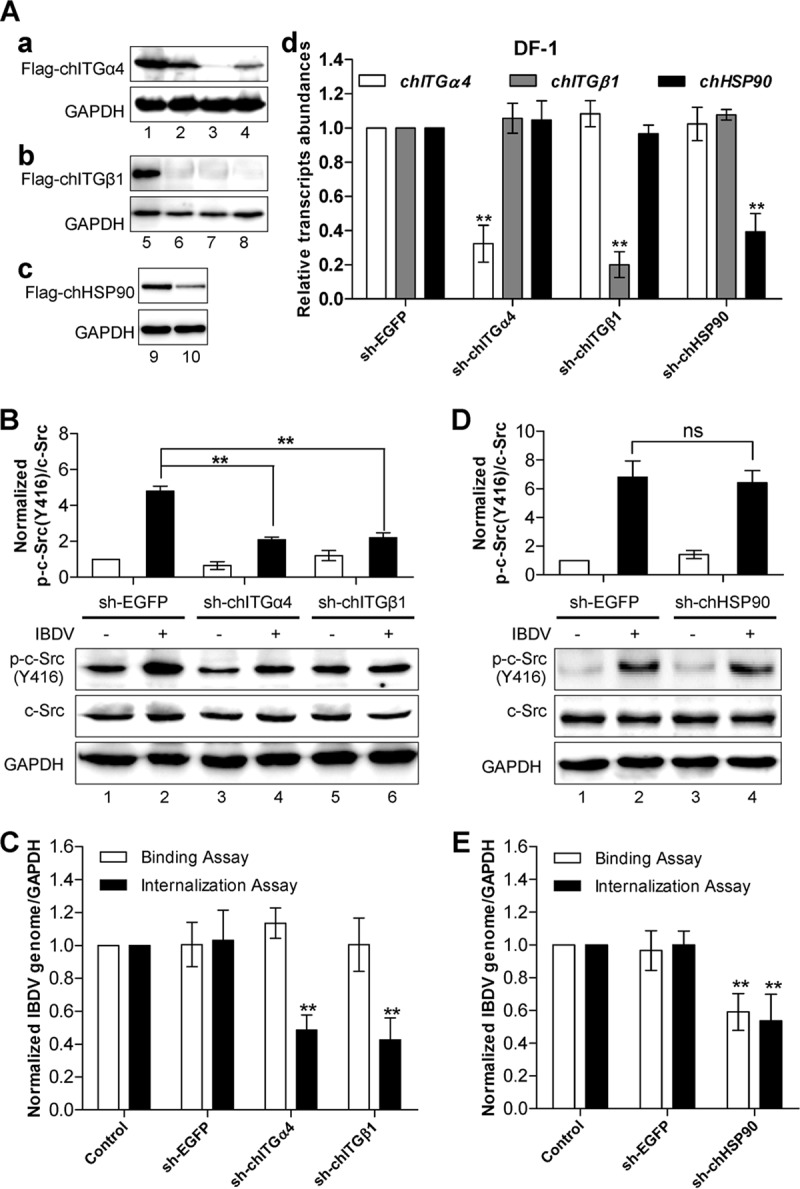
IBDV-induced c-Src phosphorylation and activation are dependent on host cell surface integrin α4β1, which is required for IBDV internalization but not for IBDV adhesion. (A) Generation of stable DF-1 cell pools with lentivirus-mediated expression of integrin ITGα4 shRNAs, integrin ITGβ1 shRNAs, HSP90 shRNA, and nontargeting EGFP shRNA as a control. shRNA-ITGα4#2 (a, lane 3), shRNA-ITGβ1#3 (b, lane 8), and shRNA-HSP90 (c, lane 10) effectively suppressed the expression of Flag-tagged ITGα4, shRNA-ITGβ1, and HSP90, respectively. GAPDH was detected as a loading control. The knockdown of the integrin subunits chITGA4 and chITGB1 or HSP90 in the stable line was confirmed by qRT-PCR, and values were normalized to the value for GAPDH (d). (B) DF-1 cells that stably expressed shRNAs against integrin α4, integrin β1, or EGFP (control) were infected with IBDV for 1 h, and the activation of c-Src was examined by Western blotting using anti-phospho-c-Src, followed by anti-c-Src and anti-GAPDH as the loading controls. The histogram shows data from densitometry analysis of the ratio of phospho-c-Src/total c-Src. (C) IBDV binding and internalization assays were performed in DF-1 cells stably expressing shRNAs against integrin α4, integrin β1, or EGFP. (D) Knockdown of HSP90 has little effect on IBDV-induced phosphorylation of c-Src. DF-1 cells with stable expression of HSP90 shRNA or control EGFP shRNA were infected with IBDV for 1 h, and the phosphorylation of c-Src was examined by Western blotting using anti-phospho-c-Src, followed by anti-c-Src and anti-GAPDH as the loading controls. The histogram shows data from densitometry analysis of the ratio of phospho-c-Src/total c-Src. (E) IBDV particle adhesion and internalization assays were performed by using DF-1 cells with stable expression of shRNA against HSP90 or EGFP. All the data are presented as means ± SDs from three independent experiments. **, P < 0.01.
