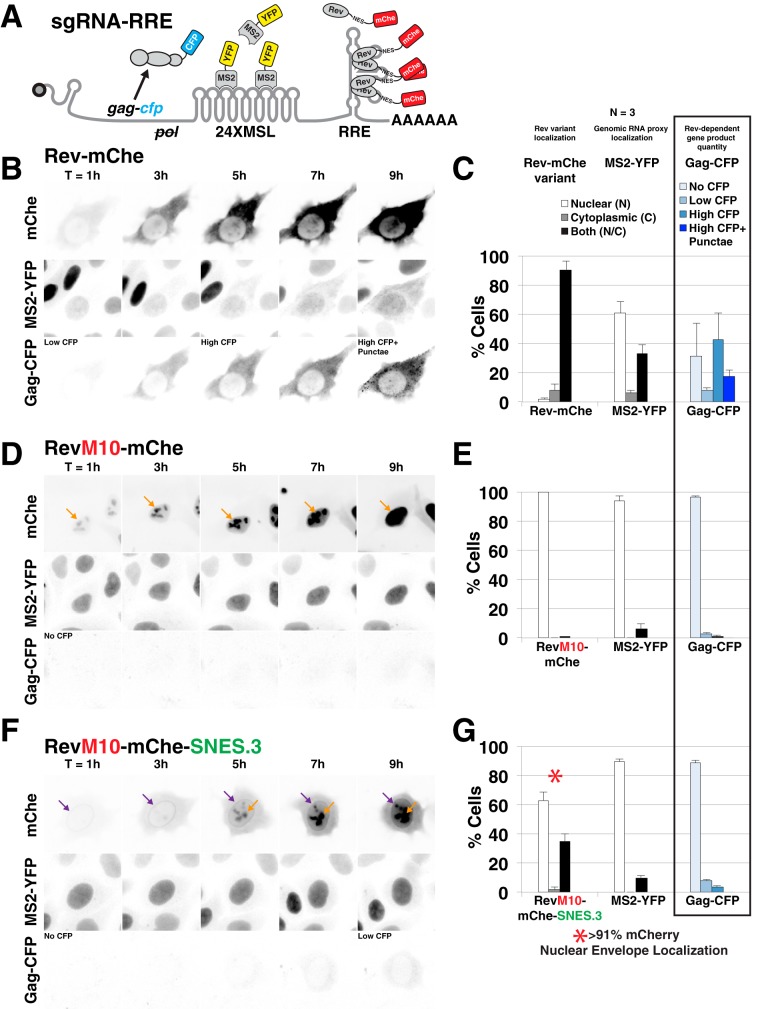
FIG 4.
SNES-arrested Rev/CRM1 complexes block Rev's ability to export vRNAs from the nucleus. (A) Diagram of subgenomic, intron-retaining HIV-1 gag-pol mRNA for live-cell imaging. This mRNA encodes 24 copies of MS2 coat protein binding loop (24XMSL) and a CFP-labeled Gag protein (Gag-CFP) for tracking Rev-dependent viral mRNA nuclear export and late viral gene expression (See Materials and Methods and reference 76 for additional information). (B to G) Live cell imaging of Rev-mChe variants, viral mRNA trafficking, and Gag-CFP expression in HeLa cells stably producing MS2-YFP (HeLa.MS2-YFP) over a 9-h interval. Image capture was initiated <1 h posttransfection and fixed at ∼24 h posttransfection for endpoint analysis. (B) Wild-type Rev-mChe supports MS2-YFP translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and Gag-CFP expression consistent with Rev-dependent viral mRNA nuclear export and translation. (C) Endpoint analysis of Rev, viral mRNA labeled by MS2-YFP proxy, and Gag-CFP. Rev and MS2-YFP distribution was quantified in individual cells for fluorescence signal as primarily nuclear (N), cytoplasmic (C), or readily detectable in both compartments (N/C). Gag-CFP was quantified based upon CFP expression level (no CFP, low CFP, or high CFP) and distribution of signal (diffuse or diffuse with punctate). Error bars represent the standard deviations from three independent transfections. A total of >300 cells were scored per condition for all transfection replicates combined. (D and E) RevM10-mChe is restricted to the nucleus (orange arrows) and does not activate viral mRNA export or Gag-CFP expression. (F and G) RevM10-mChe-SNES first accumulates at the nuclear envelope (purple arrows) and at later time points in the nucleolus (orange arrows) but does not trigger detectable viral mRNA export and supports only low levels of Gag-CFP expression. The red asterisk in panel G indicates that RevM10-mChe-SNES localization typically included signal at the nuclear envelope.