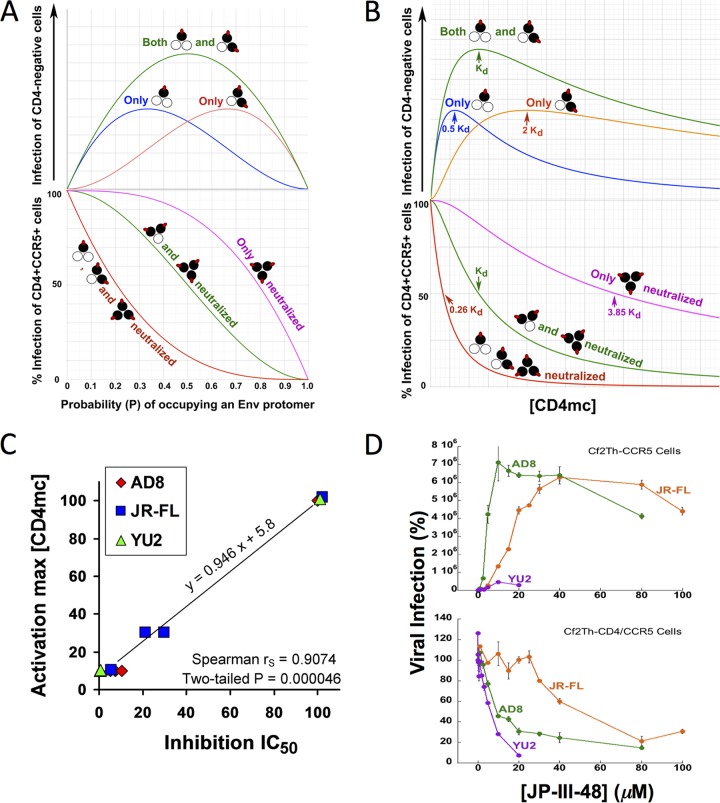
FIG 2.
Analysis of dose-response curves for CD4mc activation and inhibition. (A) Hypothetical relationship between the probability (P) of a CD4mc occupying an Env protomer and HIV-1 infection of CD4-negative, CCR5-expressing cells (top) and HIV-1 infection of CD4-positive, CCR5-positive cells (bottom) based on a binomial probability distribution. The curves shown are based on models in which the Env trimers with the indicated numbers of bound CD4mc (red ovals) are activated for infection (top) or neutralized (bottom). The protomers of the Env trimer bound by the CD4mc are colored black. (B) The hypothetical relationships in panel A are shown as a function of the free CD4mc concentration. The observation that CD4mc can sensitize HIV-1 to neutralization by antibodies (57–60) renders the model in which Env trimers with one, two, or three bound CD4mc are all neutralized improbable; nonetheless, the hypothetical curve is shown for comparison. (C) Relationship between the IC50 associated with the inhibition of infection of CD4-positive, CCR5-positive cells and the total [CD4mc] associated with maximal activation of infection of CD4-negative, CCR5-expressing cells. The Spearman rank correlation coefficient rS = 0.9074; two-tailed P = 0.000046. (D) The indicated concentrations of JP-III-48 were added to recombinant luciferase-expressing HIV-1 with the HIV-1YU2, HIV-1AD8, and HIV-1JR-FL Envs. The virus-CD4mc mixture was immediately split into two portions, with one portion added to Cf2Th-CD4/CCR5 cells (bottom) and the other portion spinoculated onto Cf2Th-CCR5 cells at 500 × g for 1 h at 25°C (top). The virus-cell mixtures were returned to 37°C, and the level of infection was determined by measuring luciferase activity in the target cells 48 h later and is shown as a percentage of the level seen in the absence of added JP-III-48. The means and standard deviations of triplicate measurements are shown. Note the correspondence between the IC50 associated with inhibition of HIV-1 infection of Cf2Th-CD4/CCR5 cells and the JP-III-48 concentration associated with maximal activation of infection of CD4-negative Cf2Th-CCR5 cells.