Figure 1.
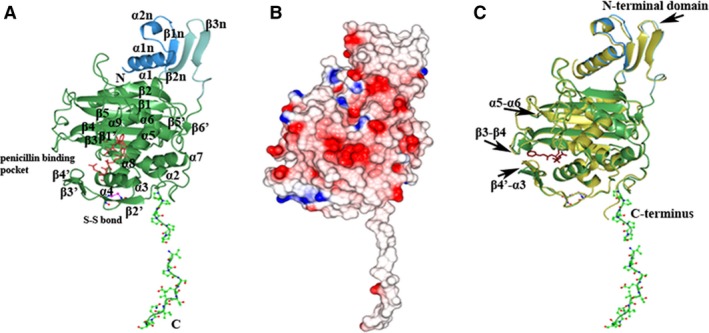
Structure of the transpeptidase domain of PonA1. (A) Ribbon diagram of the C‐terminal transpeptidase domain of PonA1 monomer from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The small adjacent N‐terminal segment of the PonA1 transpeptidase domain is colored in blue and cyan. The PonA1 penicillin‐binding domain is colored in green. Residues of the hydrophobic C‐terminal segment and cysteine residues are shown as a ball‐and‐stick model, where carbon atoms are in green (or blue for cysteines), nitrogen atoms in blue, oxygen atoms in red, and sulfur atoms in pink. Residues composing conserved motifs in the penicillin‐binding pocket of PBPs are shown as a cylinder model in crimson. The secondary structure elements are labeled. (B) Electrostatic surface representation. The surface is colored by surface potential charge from negative in red to positive in blue. (C) Comparison of PonA1 structures with (gold) and without penicillin V (green). Penicillin V is shown as a cylinder model in dark purple. The disposition of the loops in superimposed structures is marked with arrows.
