Figure 3.
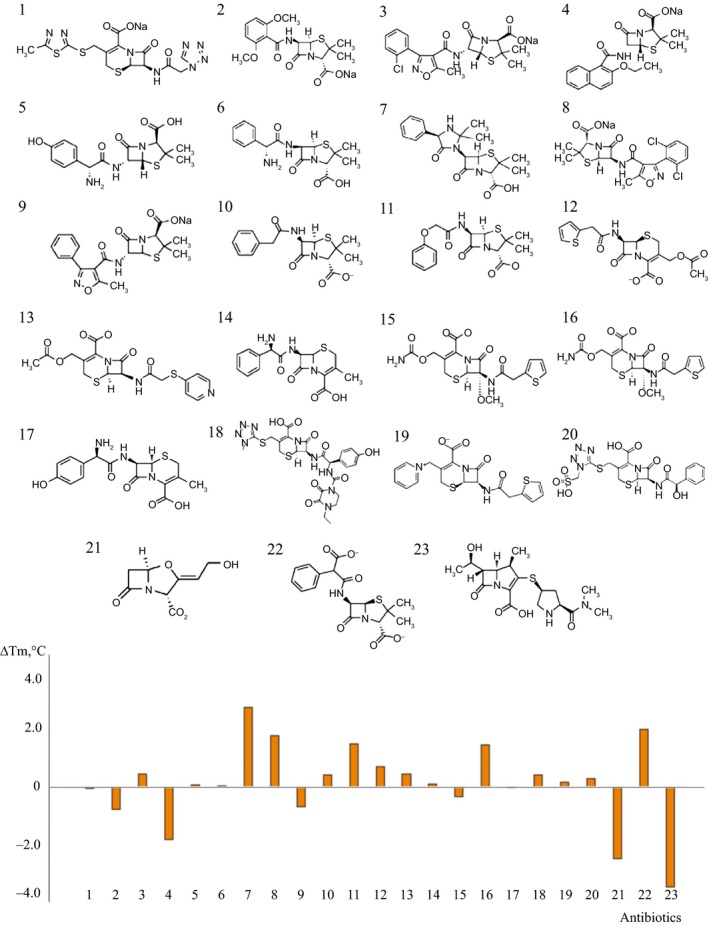
Modulation of thermal stabilities of PonA1 by different classes of antibiotics as indicated by FTS determined ΔT m. The ordinate is calculated as the difference between the T m values of PonA1 at presence and absence of antibiotics: cefazolin (1), methicillin (2), cloxacillin (3), nafcillin (4), amoxicillin (5), ampicillin (6), hetacillin (7), dicloxacillin (8), oxacillin (9), penicillin G (10), penicillin V (11), cephalothin (12), cephapirin (13), cephalexin (14), cefoxitin (15), cefotaxime (16), cefadroxil (17), cefoperazone (18), cefhaloridine (19), cefonicid (20), clavulanate (21), carbenicillin (22), meropenem (23). The data shown are for PonA1 at 2.8 μm and the antibiotics at 5 μm. Of the 23 derivatives of β‐lactam antibiotics, nafcillin, clavulanate, and meropenem give rise to significant negative T m shift indicating that these compounds make PonA1 less stable. In contrast, hetacillin, carbenicillin, dicloxacillin, and penicillin V induces the T m shift of PonA1 in the positive direction as observed for other PBP proteins.
