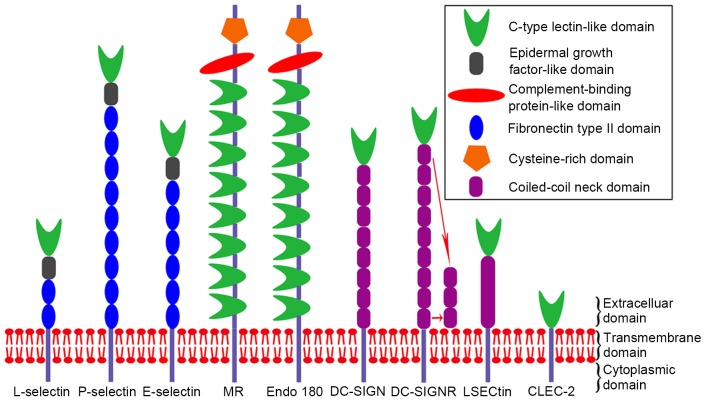
Figure 2.
Structure of C-type lectins. All molecules are transmembrane proteins with cytoplasmic, transmembrane and extracellular domains. The distinction between these proteins is concentrated in the extracellular domain. The extracellular domain of selectins comprises a CTLD, an epidermal growth factor-like domain and between two and nine fibronectin type II domains. The extracellular domain of the MR family comprises eight CTLDs, a complement-binding protein-like domain and a cysteine-rich domain. The extracellular domain of the DC-SIGN family consists of a CTLD and between one and nine coiled-coil neck domains. The extracellular domain of CLEC-2 possesses only a CTLD. The CTLD is the primary domain involved in the recognition of carbohydrates on cancer cells. CTLD, C-type lectin-like domain; MR, mannose receptor; DC-SIGN, dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3-grabbing non-integrin; DC-SIGNR, DC-SIGN-related; LSECtin, liver and lymph node sinusoidal endothelial cell C-type lectin; CLEC-2, C-type lectin-like receptor 2.