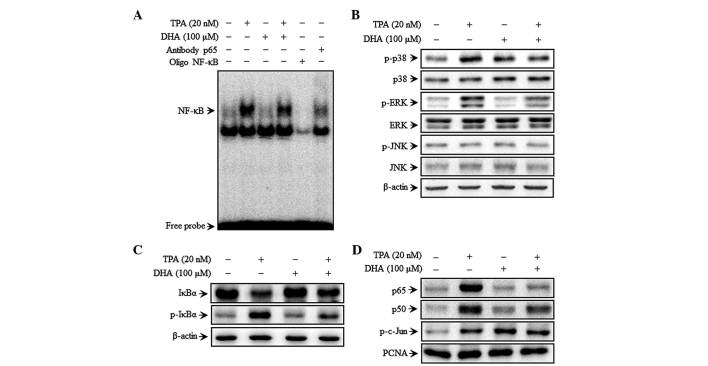
Figure 2.
DHA inhibits TPA-induced transcriptional activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and p38 phosphorylation in MCF-7 cells. Cells were treated with DHA in the presence of TPA for 4 h, followed by nuclear extraction. (A) NF-κB DNA binding was analyzed by electrophoretic mobility shift assay. (B) Cells were pretreated with TPA for 30 min in the presence or absence of DHA, and cell lysates were prepared for western blotting to detect p-p38, p38, p-JNK, JNK, p-ERK and ERK expression. (C) Cytoplasmic levels of NF-κB subunits, IκBα and p-IκBα, were determined by western blotting. (D) Nuclear levels of NFκB (p50 and p65) and activator protein 1 (p-c-Jun) subunits were determined by western blotting. TPA, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate; DHA, docosahexaenoic acid; NF, nuclear factor; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; IκB, nuclear factor of κ light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells inhibitor; p, phosphorylated; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen.