Figure 1.
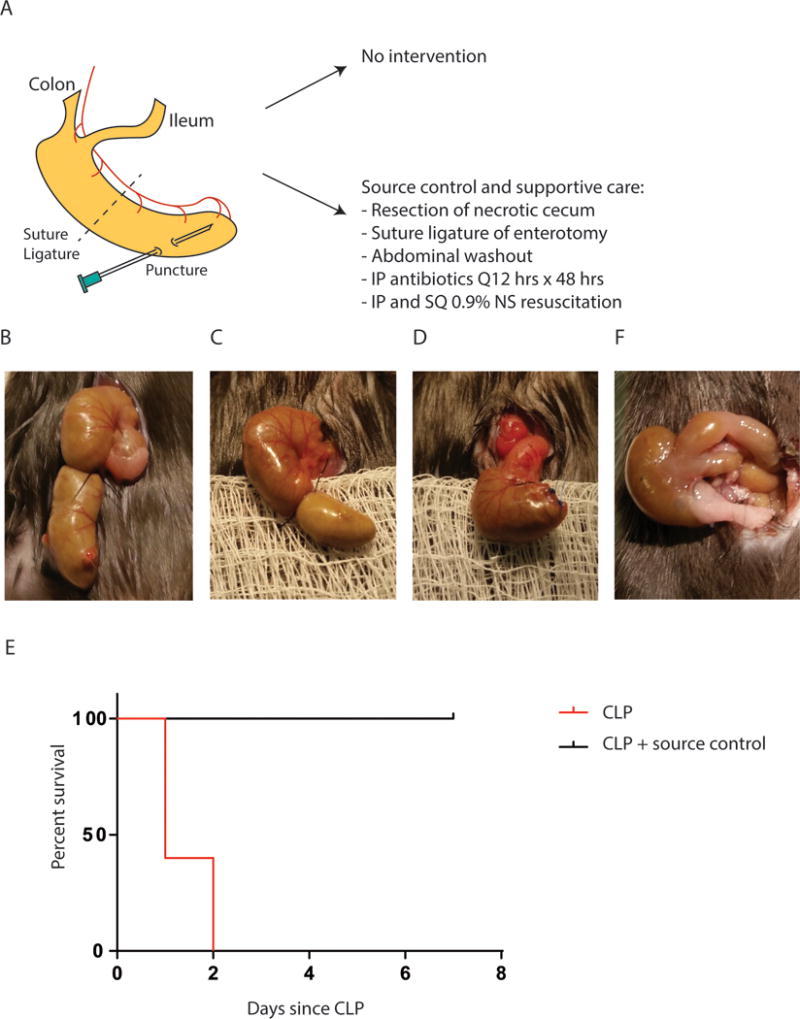
Mouse sepsis due to cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) can be reversed with proper source control. (A) Experimental design of mouse model of high grade CLP known to result in 100% mortality within 48–72 hrs (75). Following CLP, mice were divided into two groups: (1) no intervention and (2) operative source control, antibiotic treatment, and fluid resuscitation at 6 hours following CLP when first signs of sepsis are noted. (B) Appearance of cecum immediately following CLP. (C) Appearance of cecum 6 hours following CLP. (D) Appearance of cecum following surgical source control, i.e. resection of necrotic cecum and suture ligature of the enterotomy. (E) Mortality is 100% at day 2 following CLP. Source control and supportive therapy result in 0% mortality and all mice recover completely by day 7 (p=0.0023, n=5/group). (F) Appearance of cecum on day 7 following successful operative source control and supportive therapy.
