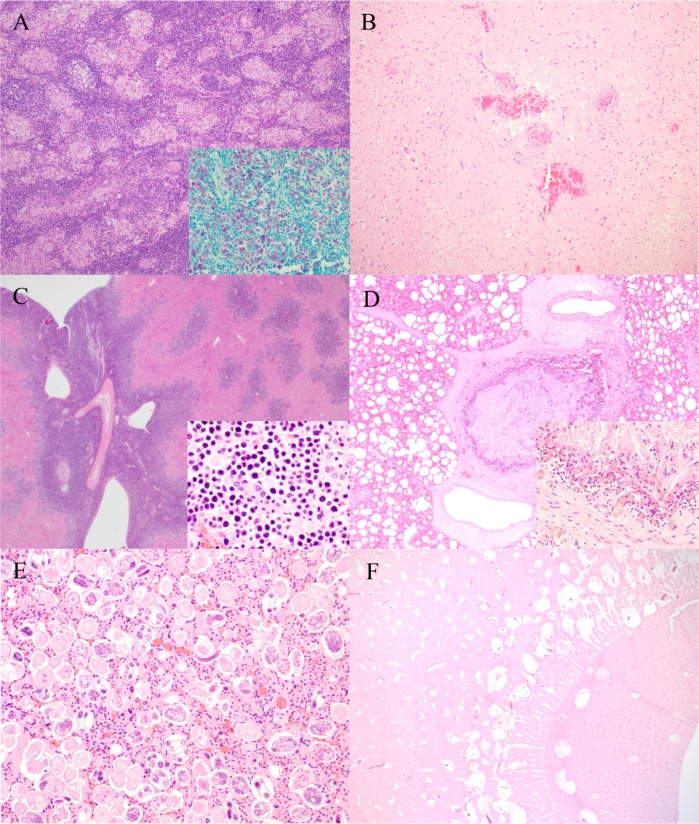
Fig 5. Selected microscopic pathology findings in free-ranging roe deer from Switzerland.
(A) Mesenteric lymph node, paratuberculosis. There are large clusters of macrophages scattered in the lymph node parenchyma. Hematoxylin and eosin. Cells contain large numbers of intracytoplamatic acid fast bacteria (Inset). Ziehl Neelsen. (B) Brain, malignant catarrhal fever. Multifocal hemorrhages often associated with variably extensive clear spaces (edema) and hypereosinophilic neurons with glassy appearence (necrotic neurons) are present in the neuropil. There is multifocal fibrinoid vascular necrosis with weak mononuclear cuffing. Prominent syncytial cells are seen in the affected vessels (Inset). Hematoxylin and eosin. (C) Liver, lymphoma. Multifocal to coalescent sheets of neoplastic cells are infiltrating the liver parenchyma. The neoplastic lymphoid cells have large basophilic nuclei with small amounts of cytoplasm and show occasional mitoses (inset). Hematoxylin and eosin. (D) Lung, acute capture myopathy. The lumen of a bronchiole is completely obscured by large amounts of mucous. The wall of the bronchus is diffusely infiltrated by often degranulating globular leukocytes, associated with hyperemic vessels surrounded by clear spaces (edema) (Inset). Hematoxylin and eosin. (E) Lung, severe lungworm infestation. The alveolar spaces are diffusely replaced by embryonated nematode eggs. Eggs contain either morulas with a variable number of cells or variably developed larvae. (F) Metatarsal bone, hypertrophic osteopathy. A thick layer of proliferating bone is expanding radially from the cortical bone. Hematoxylin and eosin.