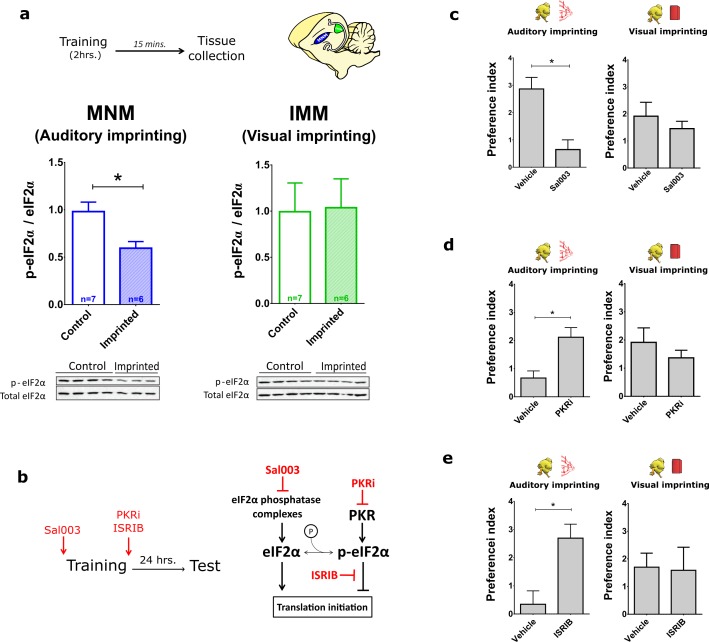
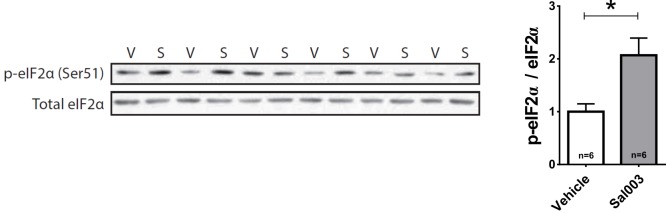
Figure 4. Translational control of auditory imprinting by eIF2α.
(a) After 2 hr imprinting training, IMM and MNM were punched out for western blot analysis. The ratio of phosphorylated eIF2α (p-eIF2α) and non-phosphorylated eIF2α was measured in controls and after training in MNM (left) and IMM (right) brain tissue. Trained chicks (n = 7) exhibited decreased eIF2α phosphorylation compared to the untrained (n = 6) in MNM but not in IMM. Representative western blots are shown below each panel. * indicates p<0.05 from unpaired Mann-Whitney test. (b) Left, drugs injected for targeting the eIF2α pathway. Right, schematic effect of pharmacological manipulations on the eIF2α pathway. (c) Auditory (left) but not visual (right) imprinting is blocked by Sal003 injection (n = 12) compared to controls injected with vehicle (n = 9). (d) Auditory imprinting (left) was enhanced in chickens injected with the PKR inhibitor PKRi (n = 26), compared to controls injected with saline vehicle (n = 14). On the other hand, PKRi (n = 26) had no effect on visual imprinting (right), compared to saline injection (n = 14). (e) Auditory imprinting (left) but not visual imprinting (right) was enhanced by ISRIB administration (n = 11) compared to controls injected with vehicle (n = 13). Bar plots represent mean and SEM, * indicates p<0.05 from unpaired t-test.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.17197.009