Figure 5.
Homozygous adl1A; E Mutants Display a Synthetic Embryo-Lethal Phenotype.
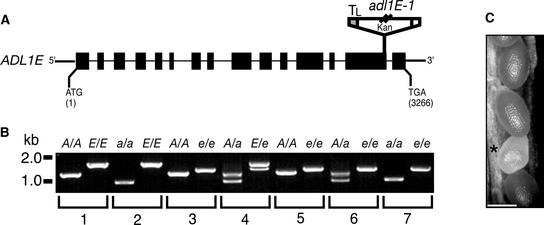
(A) Scheme of the deduced exon/intron structure of ADL1E. Black boxes and lines (drawn to scale) represent exons and introns, respectively. ATG and TGA signify the positions of the translation initiation and termination codons, respectively. The position and orientation of the T-DNA insert (not drawn to scale) in adl1E-1 is shown. Kan, T-DNA neomycin phosphotransferase selectable gene marker; TL, T-DNA left border.
(B) Genotypic analysis of the wild type and the adl1A-2, adl1E-1, and adl1A; E mutants. Total DNA was prepared from leaves (lanes 1 to 4) or isolated embryos (lanes 5 to 7) and analyzed by PCR using ADL1A–specific (A), adl1A-2–specific (a), ADL1E–specific (E), and adl1E-1–specific (e) primer sets. PCR products in wild-type [A/A; E/E] (lane 1), adl1A-2 [a/a; E/E] (lane 2), adl1E-1 [A/A; e/e] (lane 3), ADL1A/adl1A-2; ADL1E-1/adl1E-1 [A/a; E/e] (lane 4), ADL1A/ADL1A; adl1E-1/adl1E-1 [A/A; e/e] (lane 5), ADL1A/adl1A-2; adl1E-1/adl1E-1 [A/a; e/e] (lane 6), and adl1A-2/adl1A-2; adl1E-1/adl1E-1 [a/a; e/e] (lane 7) were generated from plants and embryos isolated from self-fertilized heterozygous ADL1A/adl1A-2; ADL1E-1/adl1E-1 plants.
(C) Portion of an immature silique (10 to 12 days after flowering) from an ADL1A/adl1A-2; adl1E-1/adl1E-1 plant. Genotypic analysis of genomic DNA prepared from six independent embryos isolated from the pale developing seeds (asterisk) indicated that they were homozygous adl1A; E double mutants, as shown in lane 7 of (B). Bar = 500 μm.