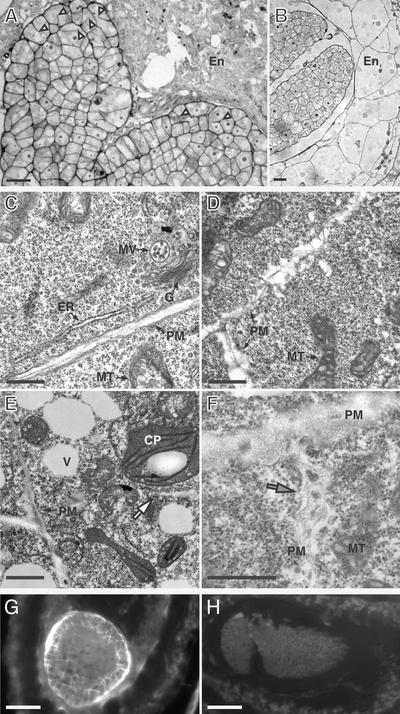
Figure 9.
Cellular Morphology of Developing adl1A; E Embryos.
(A) and (B) Histological sections of developing mutant (A) and wild-type (B) seeds containing walking stick–stage embryos and endosperm. Arrowheads in (A) indicate cytokinesis-defective protodermal cells with cell wall stubs.
(C) to (F) Transmission electron micrographs of phenotypically wild-type (C) and mutant torpedo– (D) and walking stick–stage (E) and (F) embryonic cells. The white arrow in (E) indicates a translucent cell wall stub. The mutant PM is highly irregular and encloses a thickened diffuse cell wall that contains dense inclusions (gray arrow in [F]).
(G) and (H) Transverse sections of adl1A; E (G) and phenotypically wild-type (H) sibling embryos stained with the callose binding dye aniline blue.
CP, chloroplast; En, endosperm; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; G, Golgi apparatus; MT, mitochondria; MV, multivesicular body; PM, plasma membrane; V, vacuole. Bars = 10 μm in (A) and (B), 200 nm in (B) to (E), and 40 μm in (G) and (H).