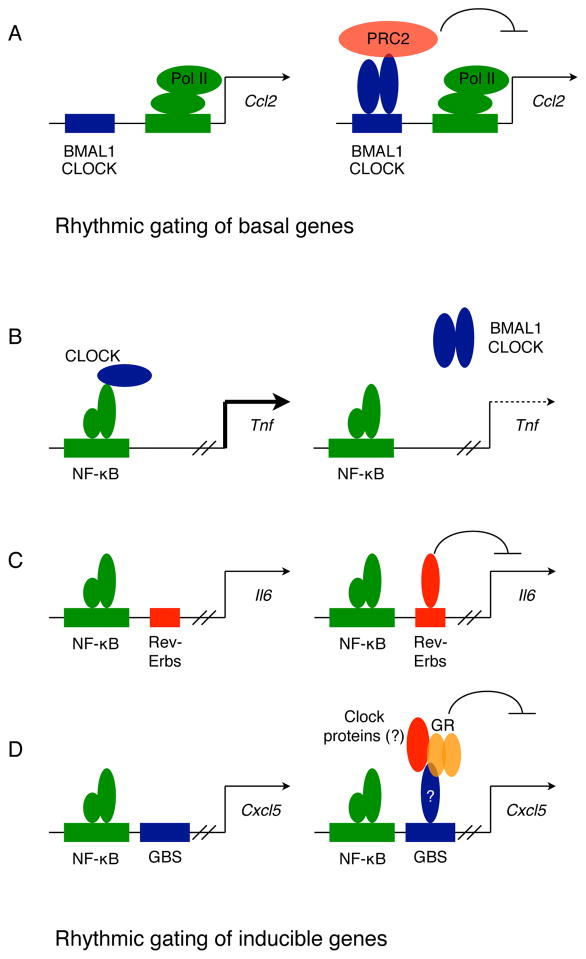
Figure 4. Models for anti-inflammatory actions of clock in myeloid cells.
(A) Rhythmic gating of basal genes. Interactions between CLOCK/BMAL1 heterodimers and the polycomb repressor complex 2 (PRC2) results in rhythmic repression of chemokine genes (such as Ccl2).
(B–D). Rhythmic gating of inducible genes. Several modes of action are proposed for rhythmic gating of LPS-induced inflammatory genes. The CLOCK protein can acetylate p65 subunit of NF-κB to induce expression of TNF, and its rhythmic sequestration by BMAL1 can drive oscillations in TNF expression (B). Recruitment of REV-ERB repressor complexes to inflammatory genes, such as Il6, can rhythmically repress their expression (C). Glucocorticoid- receptor mediated repressive effects on inflammatory chemokines requires a functional cellular clock, which may be essential for recruitment of glucocorticoid receptor (GR) complexes to glucocorticoid binding site (GBS) on the Cxcl5 gene (D).