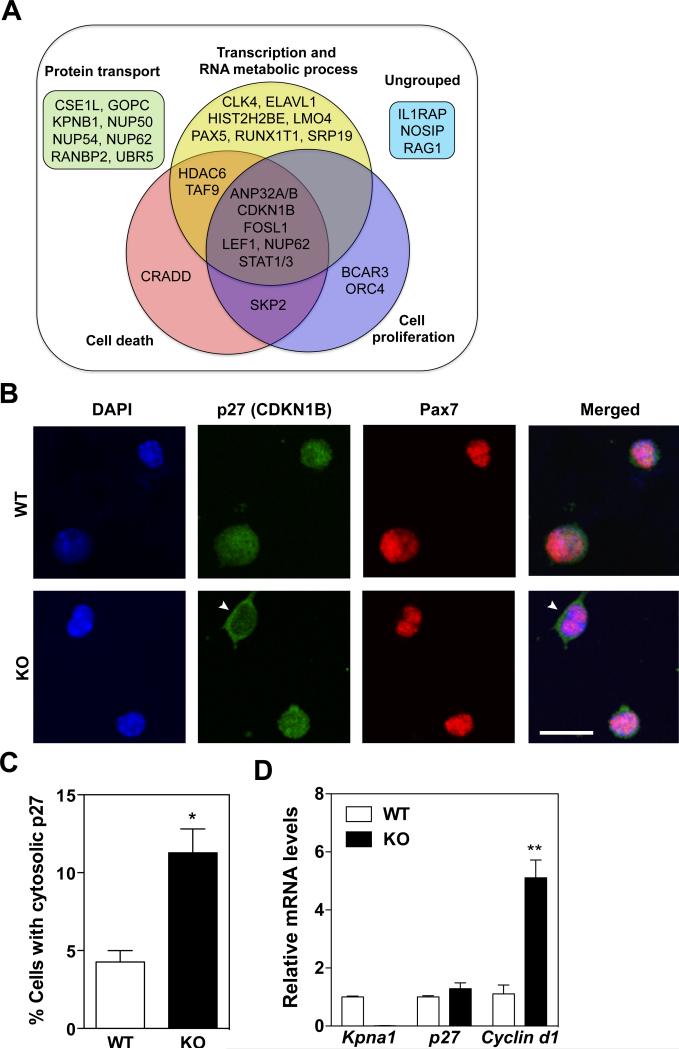
Figure 5. Reduced nuclear translocation of the cell cycle inhibitor p27/CDKN1B in KPNA1 null satellite cells.
(A) Venn diagram of 32 KPNA1-interacting proteins identified by Wiki-Pi and grouped into 4 categories by Gene Ontology (GO) analysis. (B) Representative images of p27/CDKN1B (green) and Pax7 (red) immunostaining and DAPI (blue) of wild type (WT) and KPNA1 null (KO) satellite cells isolated by magnetic activated cell sorting and cultured for 3 days. White arrowheads indicate satellite cells with cytosolic p27. Bar = 20 μm. (C) The number of satellite cells with cytosolic p27/CDKN1B immunostaining was increased 3-fold in KO relative to WT indicating impaired nuclear import of p27/CDKN1B. Approximately 400 cells were analyzed for each genotype. (D) Relative mRNA levels of Kpna1, p27, and Cyclin d1 in WT and KO isolated satellite cells. No significant difference was noted in p27 mRNA levels. The increased levels of Cyclin d1 in KO satellite cells are indicative of the increased cell proliferation observed in KO satellite cells relative to WT. Data represent the mean ± SEM. n=3 for all experiments. **p<0.01 and *p<0.05.