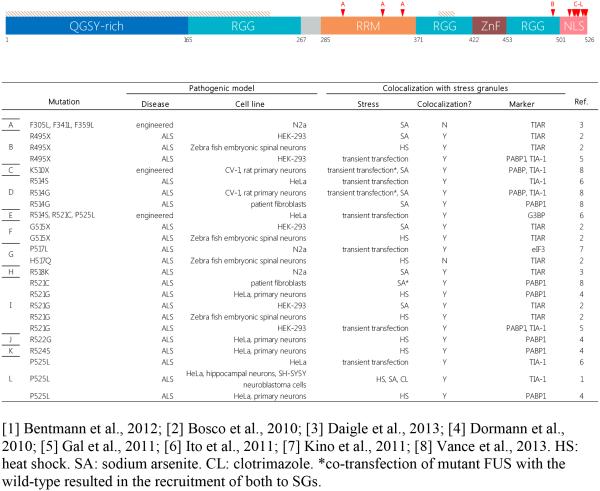
Figure 3. Schematic representation of the functional domains of FUS.
FUS is a 526-amino acid RBP with functions in transcriptional repression, DNA damage repair, and splicing. The majority of ALS-linked FUS mutations occur within its NLS, linking its mislocalization to neurodegenerative pathogenesis. Table only includes data on studied links between ALS mutations and SG association in cellular models. Mutations are marked by red arrows and letters corresponding to table entries. NLS = Nuclear localization signal; RRM = RNA recognition motif; ZnF = Zinc finger domain; RGG = Arginine-Glycine-Glycine-rich domain; Tan shading = PrLD.