Figure 1.
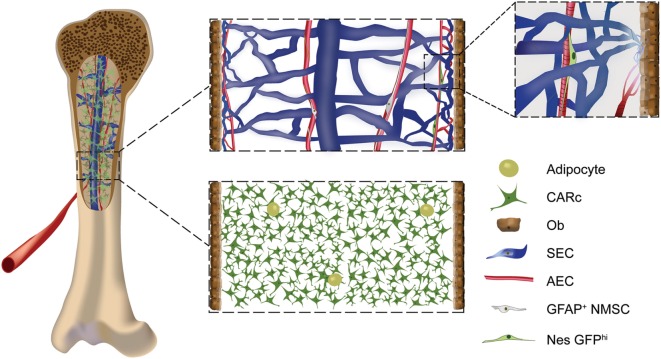
Cellular components of the stromal compartment of the bone marrow (BM): schematic overview of BM stromal cellular constituents in a mouse femur. Endothelial cells of arterial (AECs), transitional (type H), and sinusoidal [sinusoidal ECs (SECs)] subtypes form the vascular system of the BM. Densely packed AECs form arteries and arterioles, which connect to type H transitional vessels, that give rise to sinusoids made up by large SECs (upper panel, zoomed-in image). AECs, type H, and SECs have different morphological, phenotypic, and molecular features and have been shown to play specific roles in the regulation of hematopoiesis and osteogenesis. The neural component of BM stroma is formed by rare non-myelinating Schwann cells and adrenergic neurons. The mesenchymal compartment includes progenitor subpopulations such as fibroblastic reticular stromal cells, also termed CXCL12-abundant reticular cells (CARc), and Nes-GFPhi cells (upper panel, zoomed-in image). Mature mesenchymal cells are composed of bone-lining osteoblasts (Obs) and adipocytes.