Figure 8.
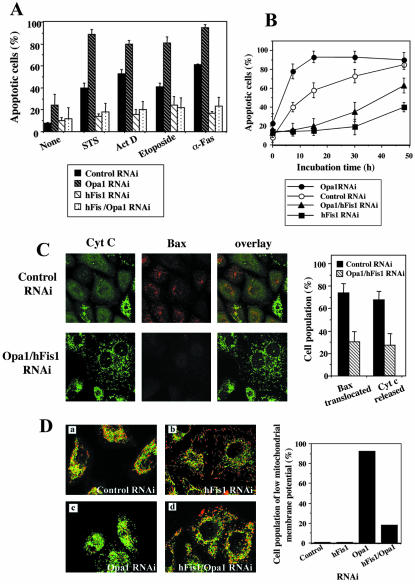
Cells depleted of both hFis1 and Opa1 show apoptosis resistance like hFis1-depleted cells. (A) HeLa cells depleted of hFis1, Opa1, or both of them by RNAi along with control RNAi cells were treated with STS (1 μM; 6 h), Act D (10 μM; 8 h), etoposide (100 μM; 30 h), or anti-Fas antibody (500 ng/ml; 15 h), and the nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342 (1 μg/ml; 15 min at RT). Normal or apoptotic nuclei of these cells in several fields were counted under the fluorescent microscope (for UV excitation). At least 200 cells altogether in each treatment were counted and plotted as a percentage of cells with apoptotic nuclei among the total cells counted. The data are shown as the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. (B) HeLa cells depleted of Opa1, hFis1, or both of them along with control RNAi cells were incubated with anti-Fas antibody (500 ng/ml) for the periods as indicated, and the nuclei were stained and counted as normal or apoptotic nuclei. At least 200 cells altogether were counted in each sample at each time point and plotted as a percentage of cells with apoptotic nuclei among the total cells counted. The data were plotted as the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. (C) Bax translocation and cytochrome c release induced by Act D treatment are inhibited in hFis/Opa1 RNAi cells. Left, HeLa cells depleted of both hFis1 and Opa1 by RNAi along with control RNAi cells were treated with Act D (10 μM; 8 h) in the presence of zVAD-fmk (50 μM), fixed, and double stained with anti-Bax (rabbit polyclonal, red) and anti-cytochrome c (mouse monoclonal, green) antibodies. Right, the number of cells displaying Bax translocation or cytochrome c release was counted and plotted as a percentage of the total cells counted in each RNAi cell population that had been treated with Act D and stained with anti-Bax and anti-cytochrome c antibodies (the same samples as shown on the left). At least 200 cells were counted altogether in several fields. Data are plotted as the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. (D) hFis1 depletion prevents mitochondrial membrane potential reduction induced by Opa1 depletion. Left, HeLa cells depleted of hFis1 (b), Opa1 (c), or both of them (d) along with control RNAi cells (a) were incubated with 5 μg/ml JC-1 for 20 min and observed by confocal microscopy. JC-1 is a cationic dye that indicates mitochondrial polarization by shifting its fluorescence emission from green to red. Regions of high mitochondrial membrane potential are indicated by red fluorescence, and regions of low mitochondrial membrane potential are indicated by green fluorescence. Right, the number of cells with mitochondria whose membrane potential was lost was counted and plotted as a percentage of the total cells counted in each RNAi cell population.