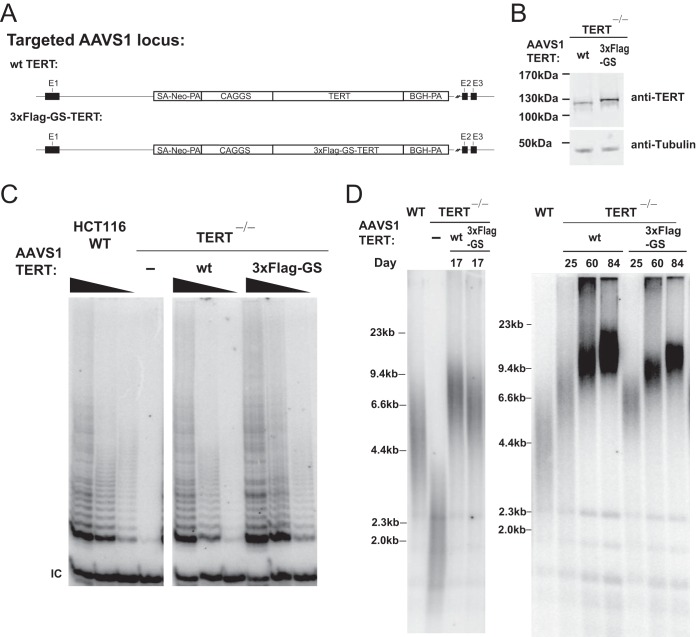
FIG 5.
Overexpression of Flag-TERT in TERT−/− cells reveals that telomere elongation was slower than that seen with wt TERT. (A) Targeting schematic of wt or 3×Flag-GS-TERT overexpression from the AAVS1 locus in the TERT knockout (KO) HCT116 cell line (TERT−/−). The TERT−/− HCT116 cell line was established by insertion of a stop codon into exon 1 of TERT using targeting vectors described previously (18). (B) Immunoblot of total TERT and tubulin protein in wt and 3×Flag-GS-TERT-overexpressing TERT−/− cells from whole-cell extracts. (C) TRAP assay of whole-cell extracts from parental HCT116 and TERT−/− cells and wt or 3×Flag-GS-TERT-overexpressing TERT−/− cells using protein titration (200, 40, and 8 ng). (D) Telomere restriction fragment assay of telomere elongation in TERT−/− cells mediated by overexpression of either wt or 3×Flag-GS-TERT at the AAVS1 locus. Data indicate the time (in days) after genome editing at the AAVS1 locus. An independent targeting experimental replicate performed for overexpression of wt and 3×Flag-GS-TERT gave the same levels of relative TRAP activity (data not shown) and telomere length differences (one replicate is shown at the left and the other replicate at the right). WT, the parental HCT116 cell line.