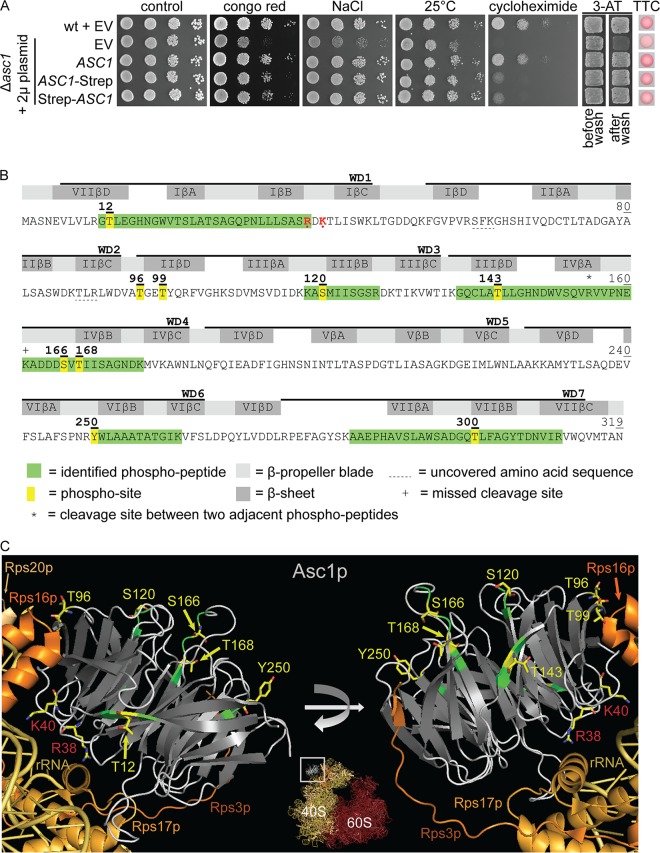
FIG 1.
LC-MS-based identification of Asc1p phosphosites. (A) Complementation of asc1− phenotypes with plasmid-borne C- and N-terminally Strep-tagged Asc1p. The Δasc1 strain was transformed with high-copy-number plasmids bearing the ASC1 wild-type gene (pME2624) or the ASC1-Strep (pME2834) or Strep-ASC1 (pME4132) allele under the control of the MET25 promoter. The ASC1 wild-type strain and the Δasc1 strain, both carrying the empty vector (EV; pME2787), served as controls. Cells were tested for their resistance to cell wall stress (Congo red), osmotic stress (NaCl), and inhibition of translation elongation (cycloheximide). The cells were additionally tested for growth at 25°C to assess temperature sensitivity. Haploid adhesive growth was tested on 3-AT. Cell patches are shown before and after washing. Respiratory activity was monitored for single yeast colonies grown on 0.4% glucose by use of the TTC assay. Apart from the reduced growth on cycloheximide, the Strep-tagged Asc1p variants complemented all asc1− phenotypes. (B) Asc1p amino acid sequence with identified phosphopeptides and phosphosites. The amino acid sequence coverage of Asc1p, considering all identified high-confidence peptides, was 97.81% (false discovery rate, ≤0.01). Phosphosites S166 and T168 were identified within a phosphopeptide ranging from residues A162 to K176 and within a second peptide from residues V156 to K176, bearing a missed cleavage site at the C terminus of K161, indicated with a plus sign. Residues R38 and K40, which lead to compromised ribosome association of Asc1p when mutated to D and E, respectively, are shown in red and marked with dots (1, 66). WD40 repeats are indicated as found in the Saccharomyces Genome Database (SGD; SMART domain SM0032). See Table S3 in the supplemental material for details on the identification of phosphopeptides and Fig. S1 for fragmentation spectra. (C) Cartoon view of Asc1p bound to the 40S subunit of the ribosome. The Asc1p β-propeller is depicted in white (loops) and gray (β-strands). Positions of phosphosites that were further analyzed in this study are highlighted in yellow, and the amino acids are depicted as sticks, with carbon atoms shown in yellow, nitrogen atoms in blue, and oxygen atoms in red. For better recognizability, neighboring amino acids within the LC-MS-identified peptides are shown in green. Additionally, residues R38 and K40 are highlighted. For the ribosomal protein Rps3, the C-terminal last 14 amino acids were not structurally resolved. Structure figures were generated with the PyMol Molecular Graphics System software on the basis of the crystal structure of the eukaryotic ribosome (Protein Data Bank [PDB] entry 4V88) (67).