Figure 1.
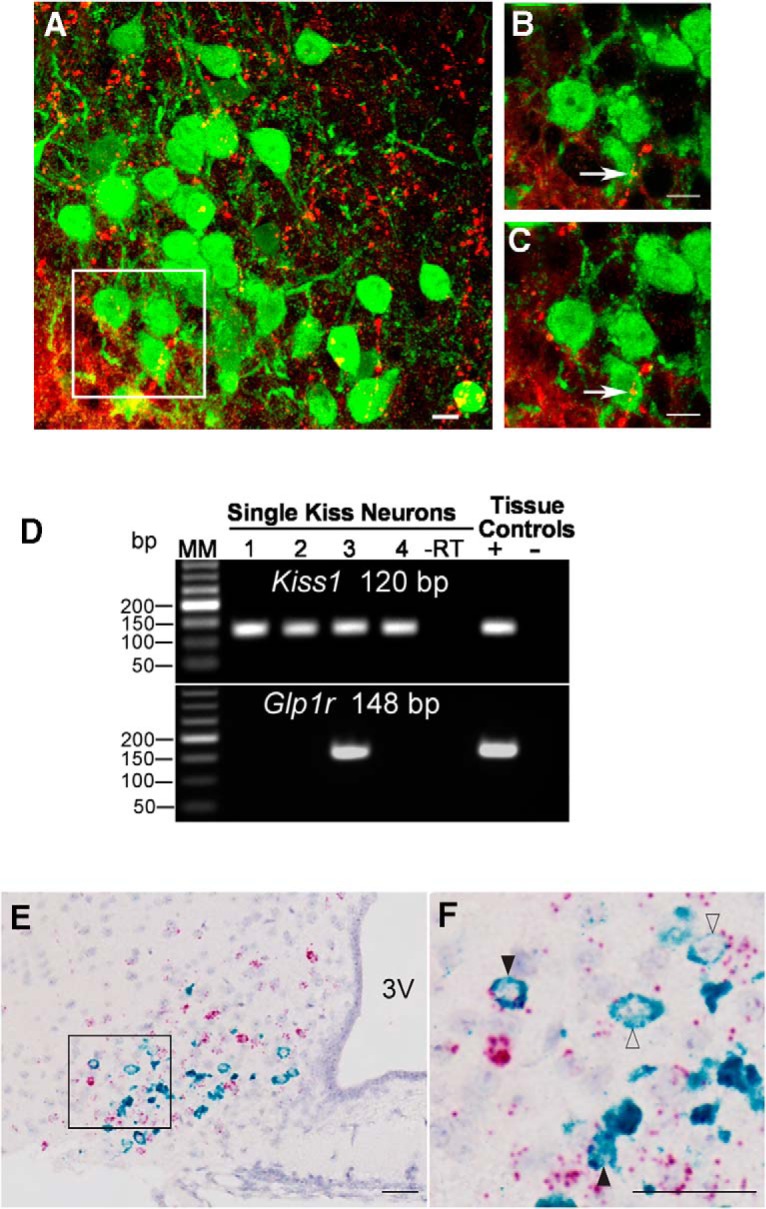
Interaction of the CNS GLP system with ARC Kiss1 in OVX mice. GLP-ir fibers (red) come in close apposition, with an average of 22% of ARC kisspeptin-ir cells (green). A, Maximal projection at 40×. B, Maximal projection at 63×. C, 1-μm plane at 63×. Scale bars = 10 μm. n = 5 animals, four sections per animal. D, Representative gel of single-cell RT-PCR demonstrating that a subpopulation (20%) of ARC Kiss1 cells from OVX mice express Glp1r mRNA. n = 5 animals, 16–33 cells per animal. The expected sizes for the PCR products are 120 bp for Kiss1 and 148 bp for Glp1r. MM, molecular marker; –RT, Kiss1-GFP cell reacted without reverse transcriptase; tissue controls (+, –), basal hypothalamic RNA reacted with (+) or without (–) RT. E, Dual ISH demonstrating coexpression of Glp1r (red) and Kiss1 (green) mRNA in the ARC (51 of 240 cells, 21.3% coexpression). In this example, an OVX animal showed robust Kiss1 mRNA expression in neurons intermingled with a larger population of Glp1r + neurons in the ARC. F, Inset of E. At higher magnification, a subpopulation of ARC Kiss1 neurons express robust and detectable mRNA signal for Glp1r. Filled black arrows, high Glp1r expression; open arrows, low Glp1r expression. n = 4 animals. Scale bars = 100 μm. 3V, third ventricle.
