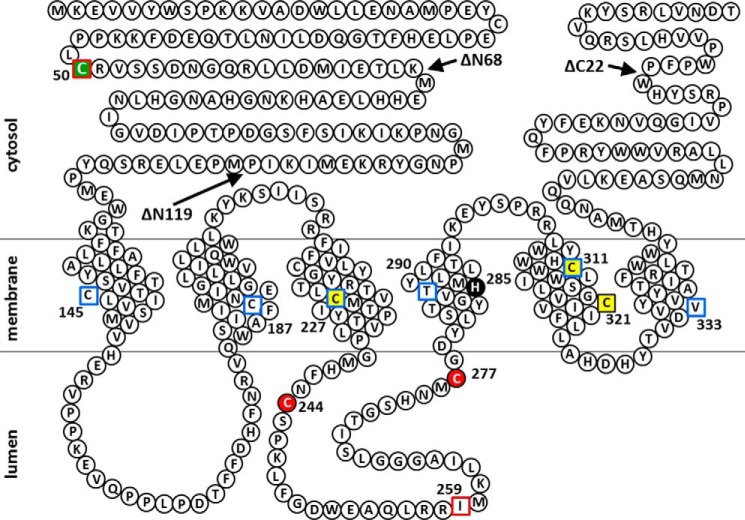
FIGURE 12.
Predicted membrane topology of human SMS1 and the positions of Cys substitutions and N- or C-terminal truncations of SMS1 mutants in this study. Snake diagram depicting the predictions of a previous report (1) and this study (Fig. 3). Cys substitutions in SMS1 that result in decreases of >80% and >20% in SMS activity compared with WT (Fig. 2E) are indicated by red filled circles and yellow filled squares, respectively. His285, a catalytic acid-base residue (48), is shown as a black filled circle. Residues in the intramembrane and non-transmembrane segments identified by the scanning cysteine accessibility method (Fig. 3F) are indicated by blue open squares and red open squares, respectively. The Cys residue responsible for homodimer formation by cysteine cross-linking (Fig. 2, A and C) is indicated by a green filled square. Arrows indicate the sites of truncation to form SMS1-ΔN68, SMS1-ΔN119, or SMS1-ΔC22.