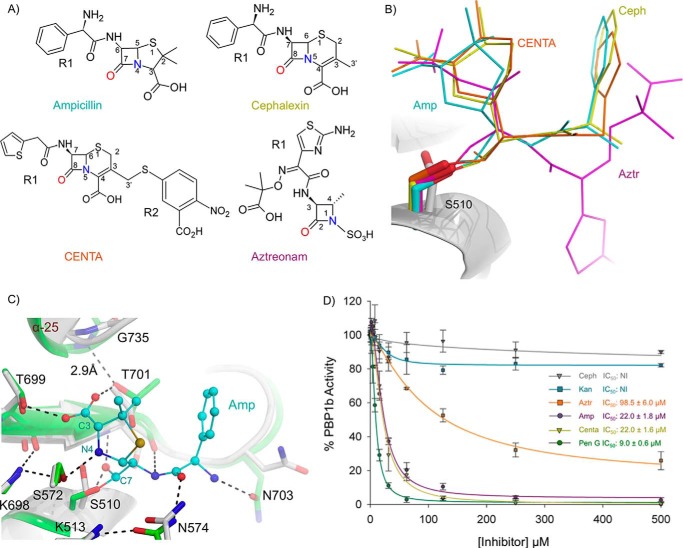
FIGURE 7.
Acyl-β-lactam E. coli PBP1b co-crystal complexes and BOCILLIN FL competition assays. A, chemical structure of β-lactams used in this study. B, overlay of acyl-β-lactam complexes. The unbound protein backbone is shown as a white cartoon. The acyl-ampicillin (Amp), cephalexin (Ceph), CENTA, and aztreonam (Aztr) ligands are depicted as teal, yellow, orange, and pink sticks. C, active site overlay of the unbound and acyl-ampicillin-bound E. coli PBP1b TPase active site. The ampicillin-bound and unbound protein backbones are shown as green and white cartoons. Key active site residues are displayed as white and green sticks with non-carbon atoms colored by type for the unbound and acyl-ampicillin-bound structures. The acyl-ampicillin (Amp) is depicted as teal sticks. Putative hydrogen bonding interactions are displayed as black dashes. D, gel-based BOCILLIN FL competition assays to analyze the ability of various unlabeled competitor compounds to bind purified E. coli PBP1b. The error bars indicate standard deviations from three separate technical replicates. NI indicates no inhibition up to 1000 μm compound. IC50 values represent the concentration of unlabeled compound required to reduce the residual binding of BOCILLIN FL by 50%.