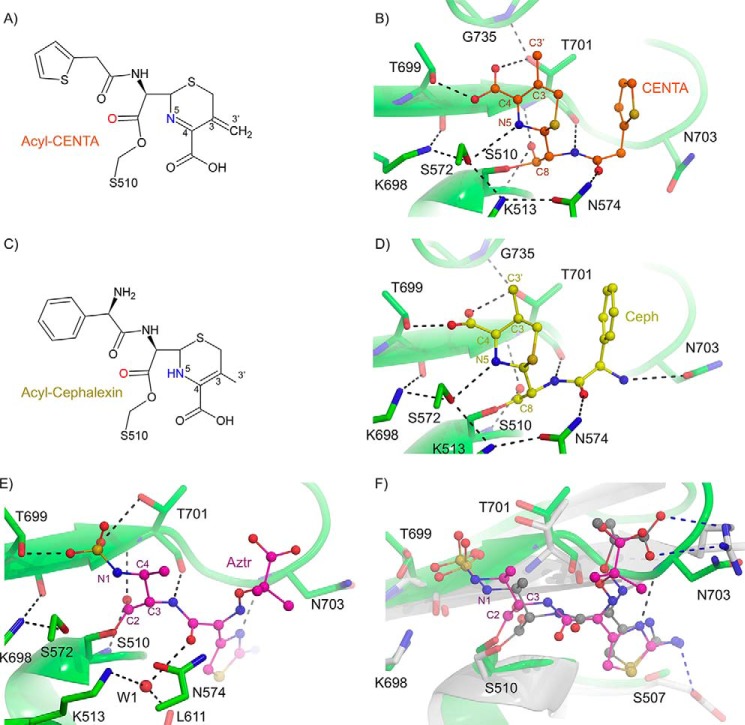
FIGURE 8.
Inhibition of E. coli PBP1b by cephalosporins and aztreonam. A, chemical structure of acyl-CENTA-bound PBP1b. B, active site close-up of CENTA-bound PBP1b. The PBP1b protein backbone is displayed as a green cartoon with key active site residues shown as sticks with atoms colored by type. C, chemical structure of acyl-cephalexin bound PBP1b. D, active site close-up of cephalexin bound PBP1b. The PBP1b protein backbone and active site residues are displayed as in B. In B and D, the CENTA and cephalexin ligands are displayed as orange and yellow sticks with non-carbon atoms colored by atom type. In B and D, putative hydrogen bonding interactions are depicted as black dashes. E, active site close-up of acyl-aztreonam bound to the E. coli PBP1b transpeptidase domain. The PBP1b protein backbone is represented as a green cartoon with key active site residues depicted as green sticks with non-carbon atoms colored by atom type. The acyl-aztreonam (Aztr) is depicted as pink sticks with non-carbon atoms colored by type. F, active site overlay of E. coli PBP1b acyl-aztreonam and P. aeruginosa PBP3 acyl-aztreonam (PDB code 3PBS). The E. coli PBP1b and bound aztreonam are displayed as in A. The P. aeruginosa PBP3 protein backbone is displayed as a white cartoon with key active site residues shown as white sticks with non-carbon atoms colored by type. The PBP3 bound aztreonam ligand is displayed as gray sticks with non-carbon atoms colored by atom type. Key ligand-protein hydrogen bonding interactions are displayed as black and blue dashes for the PBP1b and PBP3 aztreonam-bound structures. In B, residues are labeled according to E. coli PBP1b numbering.