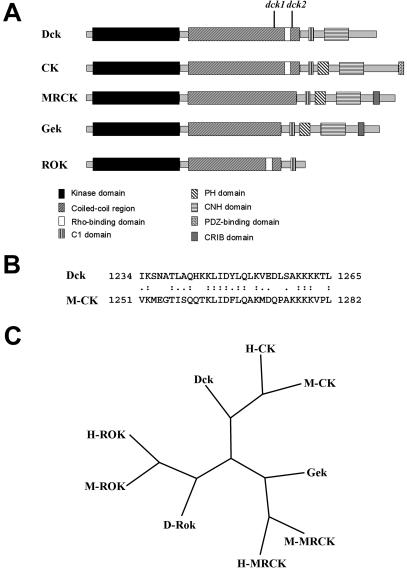
Figure 2.
Organization and evolutionary conservation of Dck. (A) Schematic representation of domain organization of the Dck protein compared with mammalian CKs, mammalian MRCK, Drosophila Gek, and mammalian ROKs. dck1 and dck2 indicate the position of the stop codons found in the corresponding mutants. The domains of Dck and evolutionarily related proteins were determined by scanning the sequence with the SMART program (Schultz et al., 1998). (B) Sequence alignment of the putative Rho binding domain of Dck with its mouse homologous sequence. The putative Rho binding domain was identified by aligning the Dck and M-CK sequences with the Smith-Waterman algorithm by using the BLOSUM 80 substitution matrix. (C) Phylogenetic tree representing the position of Dck compared with the other Drosophila (D), human (H) and mouse (M) family members. The phylogenetic analysis was performed using the maximum parsimony algorithm in the PHYLIP suite. The tree represents the consensus of a bootstrap analysis performed with 1000 replicas.