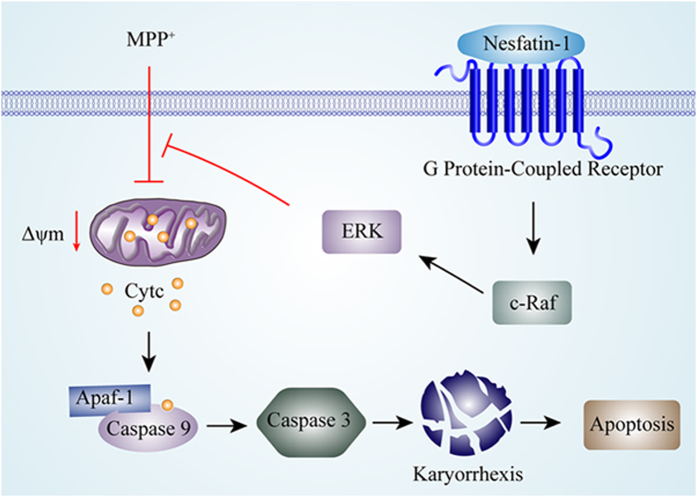
Figure 8. A schematic diagram of the mechanism underlying the neuroprotective effects of nesfatin-1 on dopaminergic neurons.
By binding to its G-protein coupled receptor and activating the C-Raf-ERK1/2 signaling cascade, nesfatin-1 antagonizes MPP+-induced apoptosis induced by mitochondrial dysfunction in dopaminergic neurons by preventing collapse of the ΔΨm, inhibiting cytochrome C releasing from the mitochondria into the cytoplasm, interacting with Apaf-1 and caspase-9, abolishing caspase-3 activation, and attenuating karyorrhexis. (Apaf-1: apoptosis protease activating factor, ERK1/2: extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1/2, MPP+:1-methyl-4-phenylpyridillium ion, ΔΨm: mitochondrial transmembrane potential).