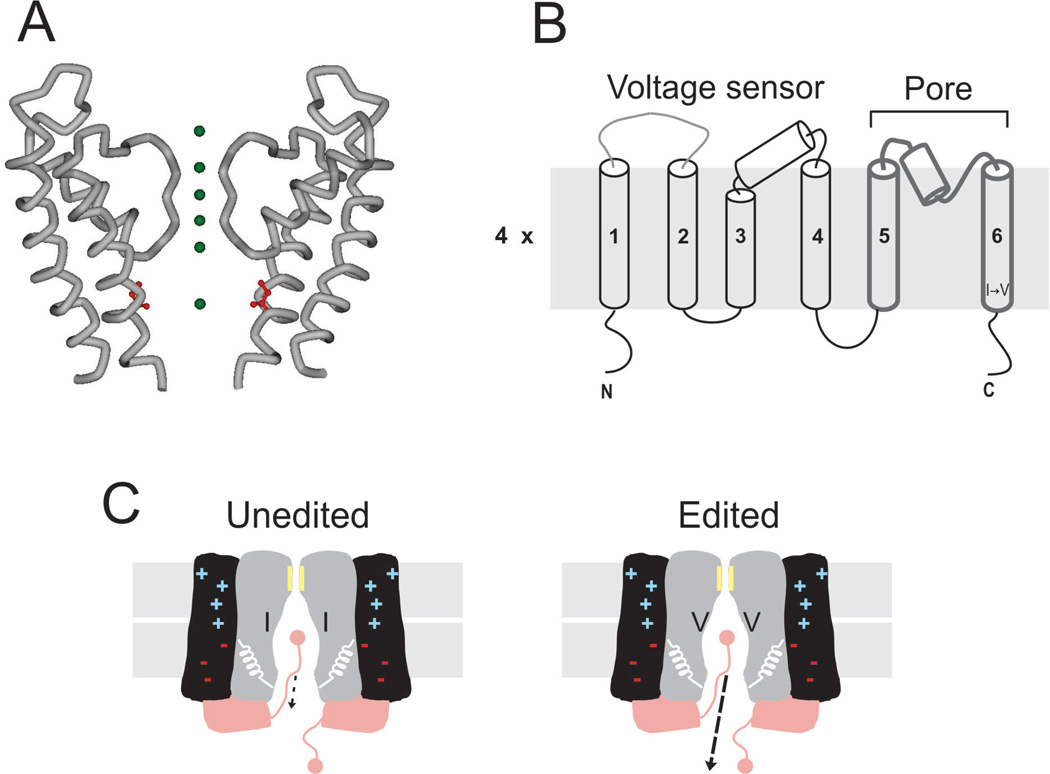
Figure 2.
RNA editing of mammalian Kv channels. (A) Crystal structure of the last two transmembrane segments from rat Kv1.2 channels (accession ID 2A79). Green spheres represent K+ along the ion permeation pathway. In red is shown the isoleucine edited by ADAR2. (B) Membrane topology of the Kv channel. A functional channel is a tetramer. In each subunit, the first four TM segments form the voltage-sensing domain, while the last two delimit the permeation pathway. The I → V edit is located at the intracellular end of the TM6. (C) Cartoon corresponding to the functional consequences of I → V substitution at the intracellular cavity of Kv channels. RNA editing targets exclusively the unbinding kinetics of the inactivation gate, increasing the off-rate by ∼ 20-fold.