Figure 2.
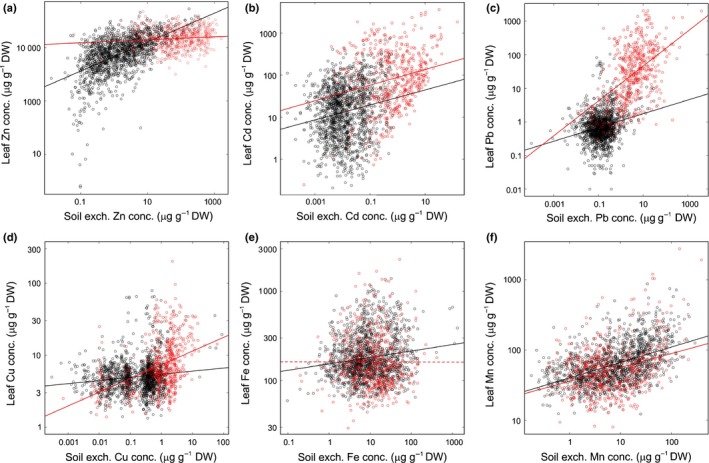
Relationships between element concentrations in leaves and local soil of Arabidopsis halleri at its natural sites of growth. (a) Zinc (Zn), (b) cadmium (Cd), (c) lead (Pb), (d) copper (Cu), (e) iron (Fe), and (f) manganese (Mn). Each datapoint represents one A. halleri individual (red: metalliferous soils, n = 506; black: nonmetalliferous soils, n = 1466), with leaves and adjacent soil (BaCl2‐exchangeable concentrations). Linear regression models are given for each soil type (continuous lines P < 0.05; dotted trendline not significant); see Supporting Information Table S2).
