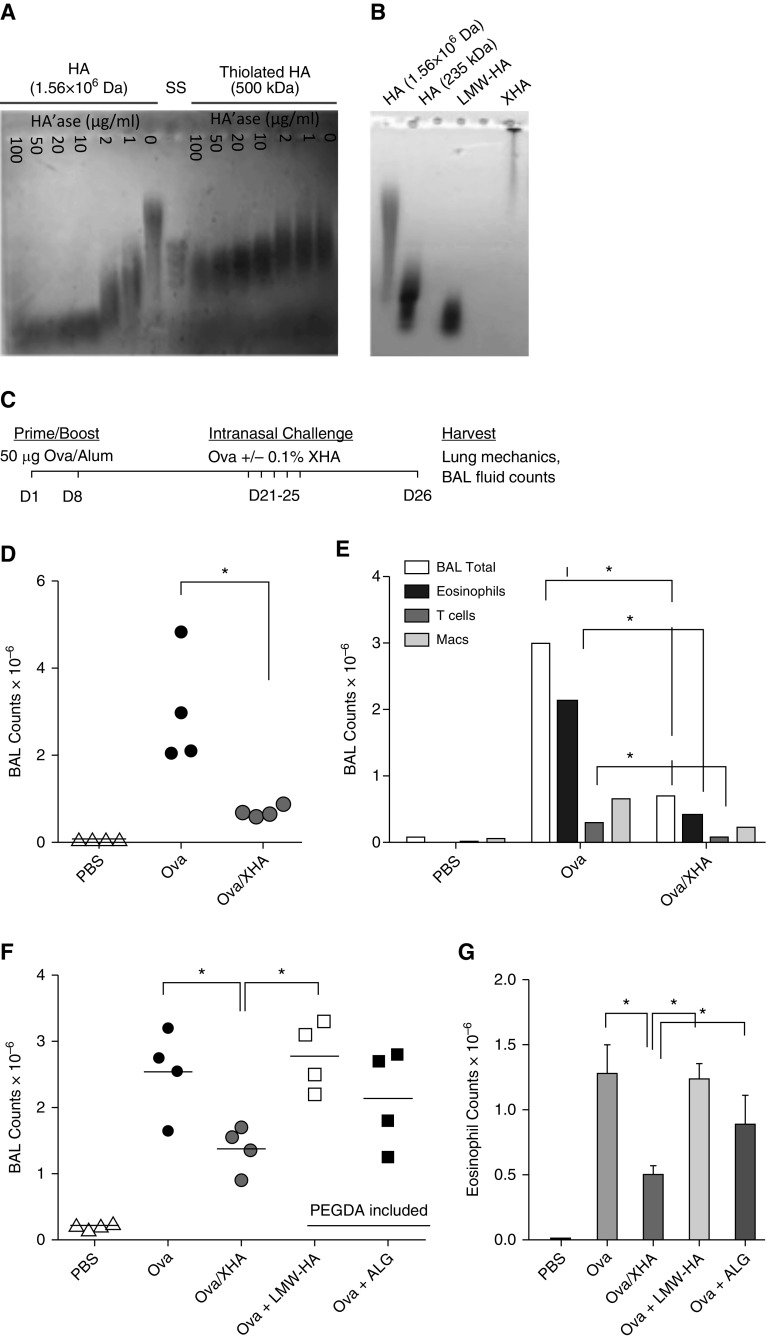
Figure 1.
Chemically modified high-molecular-weight hyaluronan (HMW-HA) (XHA) coupled with ovalbumin (OVA) (OVA/XHA) prevents allergic airway inflammation in mice previously sensitized to OVA. (A) Agarose gel electrophoresis of unmodified 1.56 × 106 443 Da HMW-HA and thiolated, 500 kD HMW-HA treated with increasing concentrations of hyaluronidase (HA’ase). A size standard (SS) ladder of 400–100 kD hyaluronan (HA) is also shown. (B) Agarose gel electrophoresis of unmodified 1.56 × 106 445 Da HMW-HA thiolated, 500 kD HMW-HA ± polyethylene (glycol) diacrylate (PEGDA) crosslinker (XHA) and controls. XHA was crosslinked overnight. All reagents were purchased commercially, and the aforementioned HA size characteristics are per the manufacturers’ information. Data in A and B are each representative of three experiments. (C) Schematic of the OVA-induced allergic airway inflammation protocol. (D) Total cell counts and (E) leukocyte subsets in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid of mice rechallenged with OVA/XHA. Data in D and E are representative of eight independent experiments. Total cell counts (F) and eosinophils (G) in BAL fluid of mice treated with OVA, OVA/XHA, low-molecular-weight hyaluronan (LMW-HA), or alginate (ALG). *P < 0.05 by Student’s t test. SE is shown. Macs, macrophages.