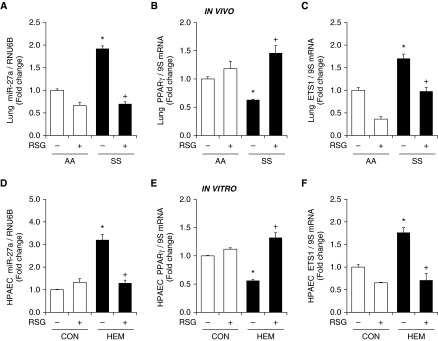
Figure 6.
The PPARγ ligand rosiglitazone (RSG) attenuates increases in miR-27a and ETS1 levels and reductions in PPARγ in SS mouse lung and hemin-treated HPAECs. (A) Whole lung homogenates were collected from AA and SS mice. Selected AA and SS mice were gavaged with RSG (10 mg/kg/d) or vehicle for 10 days. qRT-PCR was performed on AA and SS lung tissues. Lung miR-27a levels are expressed relative to RNU6B and normalized to control values. Each bar represents the mean ± SE. *P < 0.05 versus AA/−RSG; +P < 0.05 versus SS/−RSG, (n = 3–6). Lung (B) PPARγ and (C) ETS1 mRNA levels were measured with qRT-PCR and expressed relative to lung 9S mRNA levels. Each bar represents the mean PPARγ and ETS1 mRNA level ± SE expressed as fold change versus AA/−RSG. *P < 0.05 versus AA/−RSG; +P < 0.05 versus SS/−RSG (n = 3–6). HPAECs were treated with dimethyl sulfoxide vehicle (CON) or hemin (HEM, 5 μM) for 72 hours. During the final 24 hours of hemin exposure, selected HPAECs were treated with or without RSG (10 μM). HPAECs were then collected, and miRNAs or total RNAs were isolated. qRT-PCR was performed for (D) miR-27a, (E) PPARγ, and (F) ETS1 levels. Each bar represents the mean ± SE miR-27a, PPARγ, or ET-1 level relative to RNU6B or 9S as indicated. *P < 0.05 versus CON/−RSG; +P < 0.05 versus HEM/−RSG (n = 3–6).