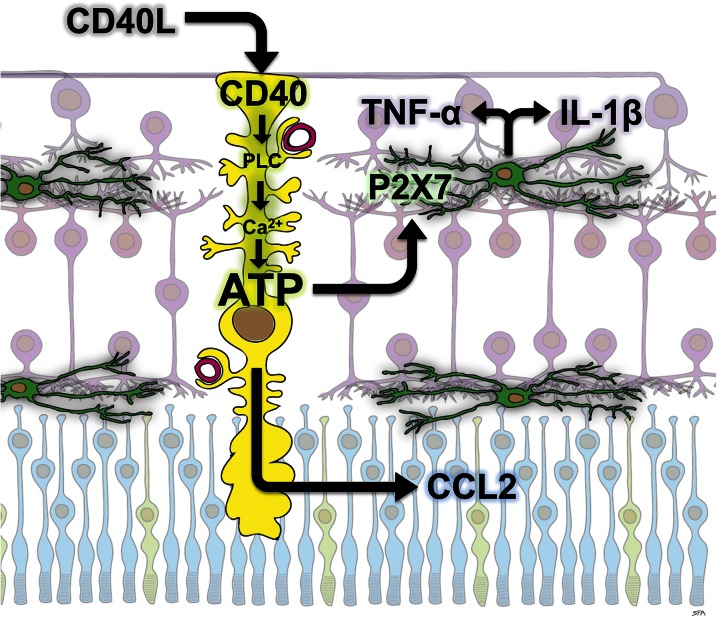
Figure 1.
Proposed role of CD40 and P2X7 receptors in diabetic retinal neuroinflammation. The CD40 receptor on Müller cells (yellow) is activated in retinas of diabetic mice, presumably by binding to CD40L. CD40 activation triggers phospholipase Cγ1 (PLC) activation, leading to an increase in intracellular calcium (Ca2+) resulting in release of ATP. CD40 activation also causes Müller cells to express the chemokine CCL2. Extracellular ATP activates P2X7 receptors on a subset of retinal microglia (green), which is necessary for their expression of the cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β. Thus, CD40 activation on Müller cells links macroglial and microglial inflammatory responses in DR.