Fig. 1.
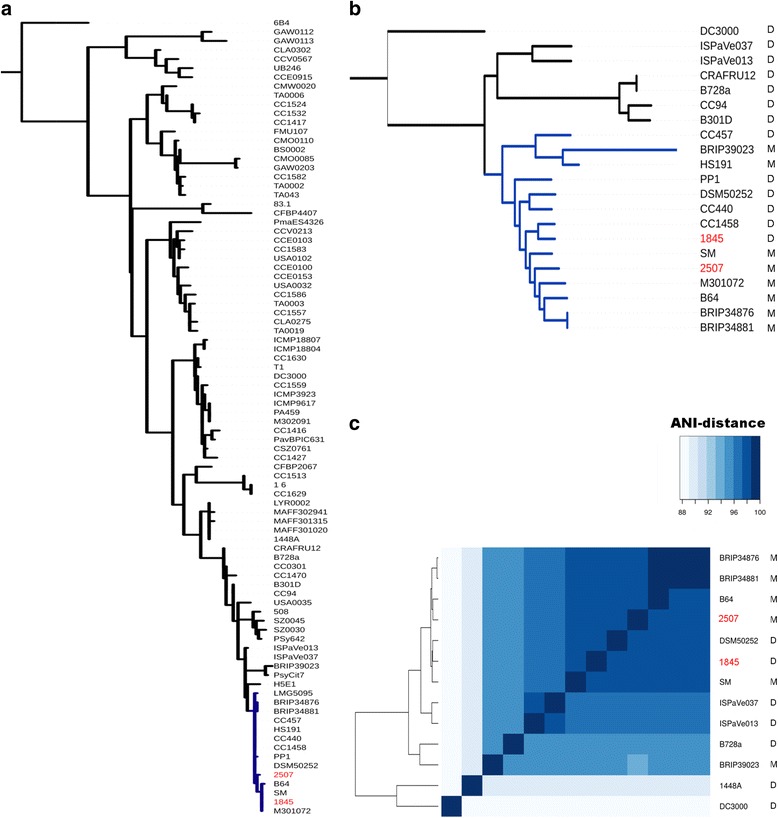
Phylogenetic analysis of strains 1845 and 2507. Russian strains are shown in red. Letters M or D indicate if a strain infects monocots or dicots, respectively. a Phylogenetic tree based on the cts gene of P. syringae 87 strains rooted on P. rhizophaerae strain 6B4. The phylogenetic tree is constructed by the maximum likelihood method using the RAxML package [22]. Clade 2b is shown in blue. b. Phylogenetic tree for 20 strains of phylogroup 2 rooted on strain DC3000. The phylogenetic tree is based on seven genes (rpoD, gltA, gap1, gyrB, kup, acnB, and pgi) with strong bootstrap support. Clade 2b is shown in blue. c Clusterization of the strains of phylogroup 2 based on the ANI values
