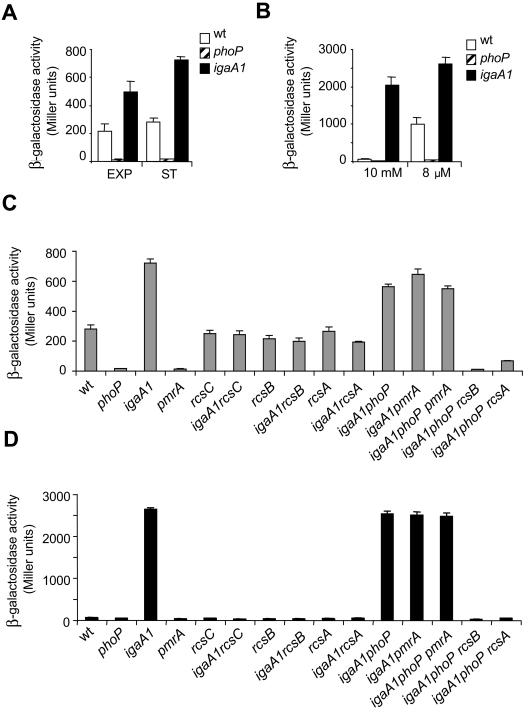
FIG. 2.
Enhanced ugd transcription displayed by the igaA1 mutant is promoted by RcsB/RcsA regulators independent of PhoP/PmrA. (A and B) Expression of a ugd::lacZ fusion inserted into wild-type, phoP, and igaA1 strains. The growth conditions were as follows: exponential (EXP) and stationary (ST) phases in LB (A) and N minimal medium containing high (10 mM) and low (8 μM) Mg2+ concentrations (B). wt, wild type. (C) Expression of the ugd::lacZ fusion inserted into wild-type and igaA1 strains lacking distinct components of the RcsC-YojN-RcsB and PhoP-PhoQ regulatory systems (RcsC, RcsB, RcsA, PhoP, PmrA). Bacteria were grown in LB to the stationary phase. (D) ugd::lacZ expression in the same series of isogenic strains as in panel C, but the strains were grown in N medium containing 10 mM Mg2+. Note that the increased ugd transcription by the igaA1 mutant was promoted by functional RcsC, RcsB, and RcsA proteins, whereas it was independent of PhoP and PmrA. The data are the means and standard errors for a minimum of three independent experiments.