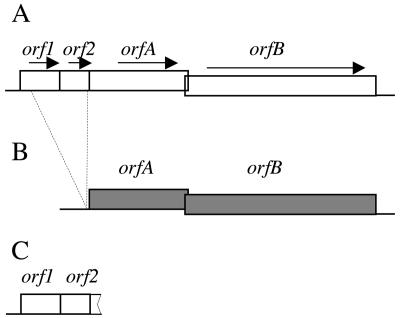
FIG. 1.
Structures of ISHp609 and related elements. (A) Full-length predominant ISHp609 type with four characteristic open reading frames and 99% DNA identity, independent of geographic origin. Sequence analysis of 10 full-length elements from Spanish strains (HUP-B43, HUP-B79, and HUP-B80; accession numbers AY487825, AY639112, and AY639113), Lithuanian strains (Lit-7 and Lit38; accession numbers AY639110 and AY639111), Alaskan strains (Al64 and Al97; accession numbers AY639115 and AY639116), a Peruvian strain (SJM27; accession number AY639118), an Indian strain (I-86; accession number AY639117), and an African strain (R48; accession number AY639114) showed limited internal divergence. In strain Lit7 orfA contained a frameshift due to a 14-bp duplication; in strain HUP-B79 orfA contained an in-frame stop codon due to a G-to-T substitution; and in strain I-86 orf1 contained an in-frame stop codon due to a C-to-T substitution. (B) ISHp609var. This rare variant element was found in one Indian strain (Chennai4; accession number AY639119) with 81% DNA identity to the predominant type. ISHp609var has full-length orfA and orfB genes, although orfB is probably inactive due to a frameshift. It lacks orf2 and most of orf1, and it has the first 79 bp of orf1, but there is no start codon at its left end. (C) orf1-2 remnant. This DNA segment consists of orf1 (jhp960 in strain J99), orf2 (jhp961 in strain J99), and the first 37 bp of orfA and is located between homologs of jhp959 and jhp962 in most or all strains (as determined by PCR with primers jhp959 and jhp962, primers jhp959 and 609.R6, and primers FlankL and jhp962).