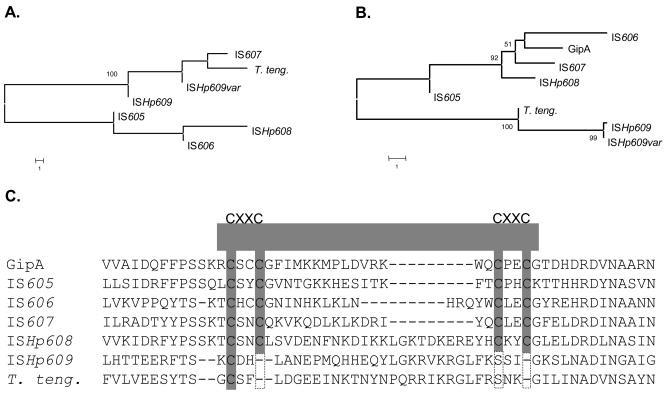
FIG. 2.
Phylogenetic relationships among H. pylori IS elements. (A) OrfA and homologs. Two subfamilies were identified, one represented by OrfAs of IS605 (accession number NP_208326), IS606 (accession number AAD11513), and ISHp608 (accession number AAL06576), which are not considered to encode serine recombinases based on amino acid homologies, and the other represented by IS607 (accession number AAF05600), ISHp609 (accession number AAR83266.1), ISHp609var (accession number AY639119), and the closest homolog in T. tengcongensis (T. teng.) (tte0714; accession number AAM23976), which are thought to encode serine recombinases. Branches with significant bootstrap support (≥50) are indicated. Bar = 1 amino acid substitution per site. (B) OrfB and homologs. OrfBs of H. pylori IS605 (accession number NP_208324), IS606 (accession number AAD11514), IS607 (accession number AAF05601), ISHp608 (accession number AAL06577), and Salmonella's GipA protein (accession number NP_752781) form an OrfB subfamily different from that of ISHp609 (accession number AAR83267.1), ISHp609var (accession number AY639119), and the closest homolog in T. tengcongensis (tte0715; accession number AAM23977). (C) Partial C-terminal sequence alignment of H. pylori IS element OrfBs, GipA (22), and the corresponding sequence in T. tengcongensis. A single C-terminal Zn(II) binding tetracysteine motif, CX(2)CX(15)CX(2)C (C4-type zinc finger), is well conserved among IS605, IS606, IS607, and ISHp608 OrfBs and GipA and might potentially facilitate DNA or RNA binding or protein-protein interaction. Notably, this motif is not present in ISHp609 OrfB (both predominant and variant).