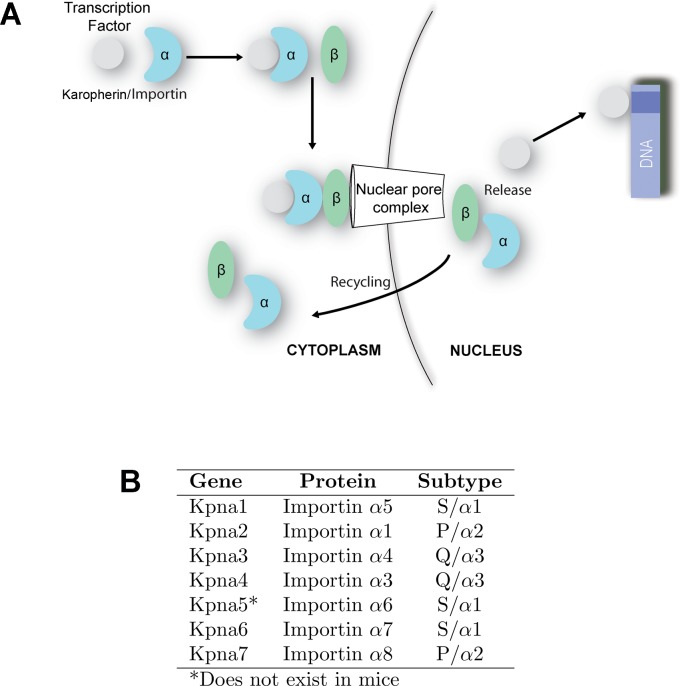
Fig 1. Karyopherin alphas in canonical nuclear import.
(A) In canonical import, a karyopherin α (Kpna) binds to both the nuclear localization sequence-containing cargo protein and to Kpnb. Subsequently, Kpnb interacts with the nuclear pore to bring the trimeric complex into the nucleus. Once within the nucleus, the complex dissociates, and Kpna and Kpnb are recycled to the cytoplasm. (B) Seven Kpna genes encoding Kpna proteins have been identified in humans, and six in mice. They belong to three subtypes based on homology. Nomenclature for each corresponding Impα protein is indicated. While nomenclature of the paralogs varies in different studies, we will use the human Kpna designations for clarity.