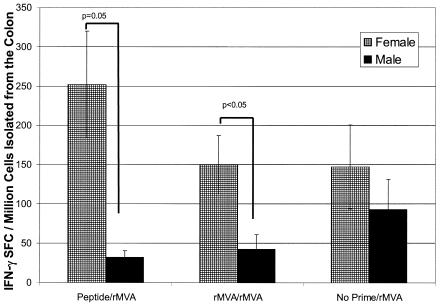
FIG. 3.
Antigen-specific IFN-γ-producing lymphocytes isolated from the colon of female and male BALB/c mice following prime-boost immunization. Female and male mice were primed with either peptide (50 μg) with cholera toxin i.n. or MVA (107 PFU) i.d. All animals were boosted with MVA (107 PFU) i.d. Twenty days after MVA boosting, colon lymphocytes were isolated and assayed for the frequency of P18-specific IFN-γ-producing cells by ELISpot. Due to low yields of cells from individual mice, cells isolated from four mice were pooled. Each bar represents the mean ± standard error of six pooled sets of colon tissue (specimens from 24 mice). Lymphocytes isolated from the colons of females primed with peptide and boosted with rMVA had a significantly higher frequency of IFN-γ SFCs than did lymphocytes isolated from the colons of males primed and boosted via the same regimen (P = 0.05 by ANOVA). (Although ANOVA revealed no significance between females and males receiving rMVA-rMVA, Student's t test showed P values of <0.05).