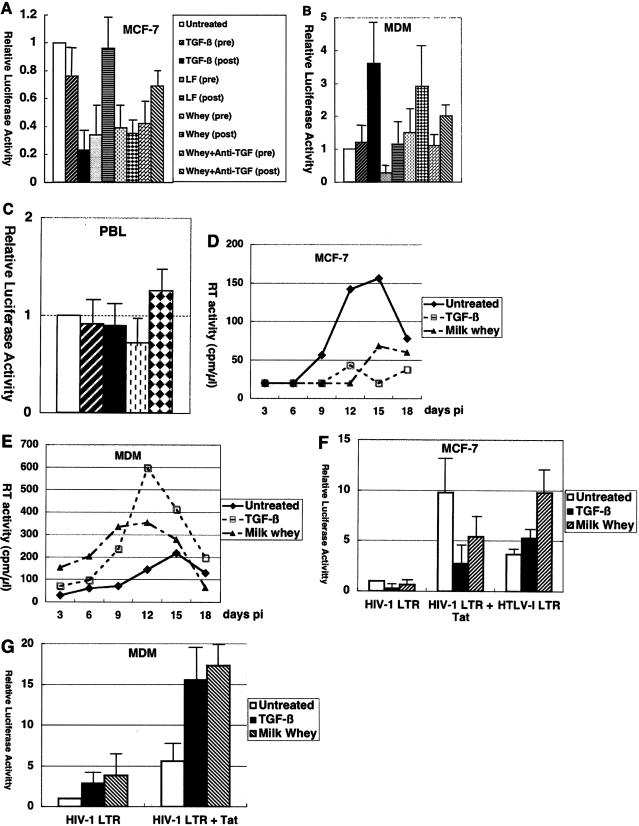
FIG. 2.
Cell type-dependent effects of TGF-β on HIV-1 infection. (A, B, and C) In single-round viral replication assays, TGF-β inhibited HIV-1 infection of MCF-7 cells, enhanced HIV-1 infection of monocyte-derived macrophages at a postentry step(s), and had a minimal effect on HIV-1 infection of peripheral blood lymphocytes. MCF-7 cells (A), monocyte-derived macrophages (B), and peripheral blood lymphocytes (C) were either untreated or treated for 16 h before infection (pre) or treated after infection (post) with NL4-3-Luc-R−E− supplemented with Envglycoprotein from 89.6 with TGF-β (200 pg/ml), human lactoferrin (LF) (100 ng/ml), or crude milk whey (10%) with and without anti-TGF-β antibody (10 μg/ml). Cells were harvested 48 h after infection, and cell lysates were subjected to luciferase assays. Arbitrary light units are shown. Error bars represent standard deviations from duplicate experiments. (D, E) In multiple-round viral replication assays, TGF-β inhibited HIV-1 infection of MCF-7 cells and enhanced HIV-1 infection of monocyte-derived macrophages. Approximately 2 × 105 MCF-7 cells (D) or 4 × 105 monocyte-derived macrophages (E) were untreated or treated with TGF-β (200 pg/ml) or crude milk whey (10%) for 16 h before and continuously after infection with HIV-1 89.6. The experiments were repeated twice with similar results. Another experiment in which monocyte-derived macrophages were also infected with ELI1 also gave similar results (data not shown). (F, G) Cell type-dependent effects of TGF-β on HIV-1 LTR activity. MCF-7 cells (F) and monocyte-derived macrophages (G) were transfected with pGL-HIV-1-LTR and pSV2-CAT, pGL-HIV-1-LTR and pSV2-Tat, or pHTLV-I-luc and either untreated or treated with TGF-β (200 pg/ml) or crude milk whey (10%). Results are shown as luciferase activity relative to that of pGL-HIV-1-LTR and pSV2-CAT when untreated. Error bars represent standard deviations from triplicate experiments.