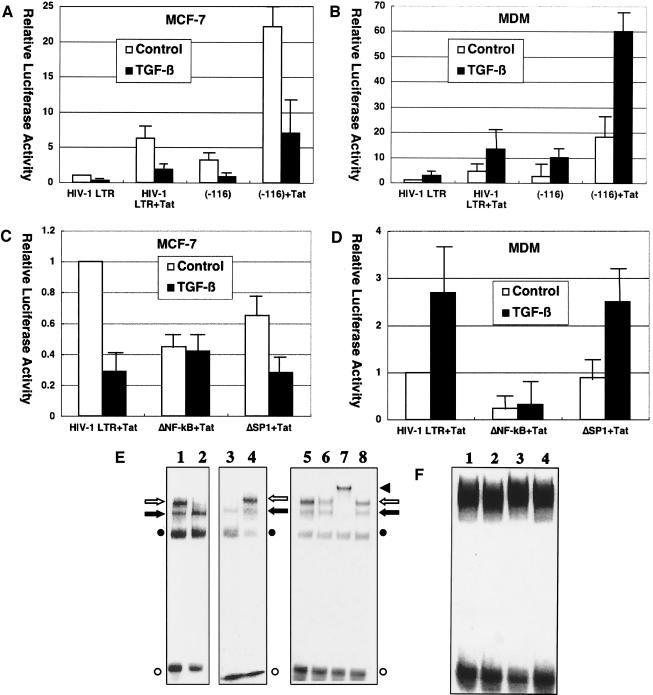
FIG. 4.
TGF-β effects on HIV-1 infection are mediated by NF-κB activity. (A to D) Critical role of NF-κB binding sites in TGF-β-mediated effects on HIV-1 LTR. MCF-7 cells (A) or monocyte-derived macrophages (B) were transfected with pGL-HIV-1-LTR or pGL-HIV-1-LTR(−116) along with pSV2-Tat and either untreated or treated with TGF-β (200 pg/ml). Also, MCF-7 cells (C) or monocyte-derived macrophages (D) were transfected with pGL-HIV-1-LTR, pGL-HIV-1-LTRΔNF-κB, or pGL-HIV-1-LTRΔSP1 along with pSV2-Tat and either untreated or treated with TGF-β (200 pg/ml). Error bars represent standard deviations from triplicate experiments. (E, F) TGF-β effects on NF-κB binding to HIV-1 LTR. (E) 32P-labeled oligonucleotides corresponding to sequences spanning the HIV-1 LTR NF-κB binding sites were incubated with nuclear extracts (15 μg of protein) from MCF-7 cells (lanes 1, 2, and 5 to 8) or monocyte-derived macrophages (lanes 3 and 4) and analyzed by gel mobility shift assays. Those cells were either untreated (lanes 1 and 3) or treated (lanes 2 and 4 to 8) with TGF-β (200 pg/ml) for 10 min before harvest. In addition, anti-p65 antibody (lane 6), anti-p50 antibody (lane 7), or control serum (lane 8) was added to the reaction. An open arrow and a solid arrow indicate the p50/p65 heterodimer (NF-κB) and p50 homodimer, respectively. An open circle and a solid circle indicate free probe and nonspecific complex, respectively. A solid triangle indicates a complex supershifted by anti-p50 antibody. (F) 32P-labeled oligonucleotides corresponding to sequences spanning the HIV-1 LTR SP1 binding sites were incubated with nuclear extracts from MCF-7 cells (lanes 1 and 2) or monocyte-derived macrophages (lanes 3 and 4) and analyzed by gel mobility shift assays. Those cells were either untreated (lanes 1 and 3) or treated with TGF-β (200 pg/ml) for 10 min before harvest (lanes 2 and 4).