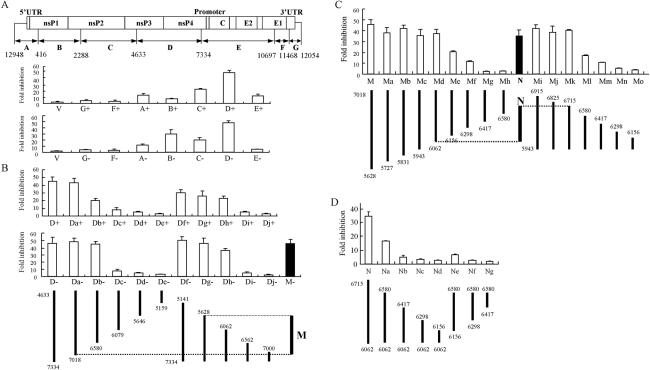
FIG. 2.
Mapping the target sequences of ZAP in the SIN genome. The test sequences of SIN were cloned into pGL3-Luc-linker between the luciferase coding sequence and the poly(A) signal in either a (+) or (−) orientation. The numbers indicate the positions of the ends of the fragments in the SIN genomic clone. The constructs were transfected into Rat2-HA-Zeo or Rat2-NZAP-Zeo cells. At 48 h posttransfection, the cells were lysed and analyzed for inhibition as described in the legend to Fig. 1. The data are means plus SD of at least three independent experiments. (A) The infectious clone of SIN was divided by restriction digestion into fragments, designated as indicated, and each fragment was tested for inhibition. V, control vector pGL-3-Luc-linker. (B) The D fragment from panel A was truncated from the 5′ or 3′ end, as indicated, and analyzed for inhibition. M, a fragment of D retaining most of the sensitivity. (C) The M fragment from panel B was truncated from the 5′ or 3′ end, as indicated. The fragments were cloned into pGL3-Luc-linker in the antisense orientation. N, a fragment retaining most of the sensitivity of M. (D) The N fragment from panel C was further analyzed by deletion mutagenesis, as indicated. The fragments were cloned into pGL3-Luc-linker in the antisense orientation.