FIG. 2.
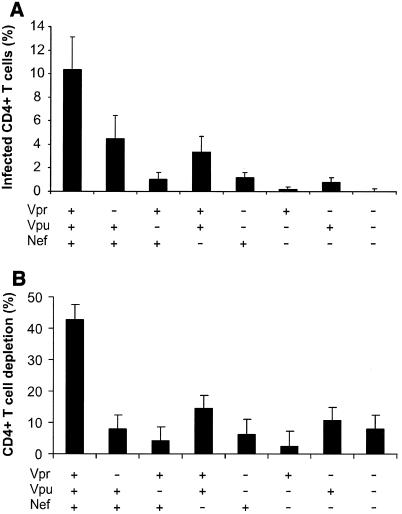
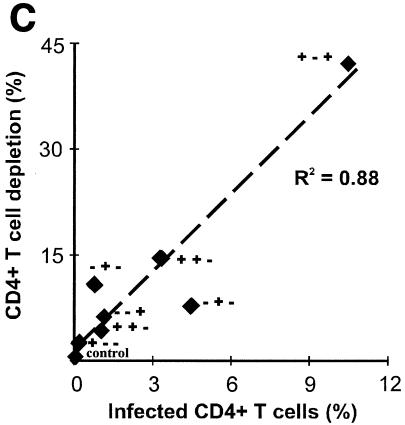
CD4+-T-cell depletion in human lymphoid tissue infected ex vivo with HIV-1 variants. (A) Percentages of infected cells; (B) loss of CD4+ T cells in human lymphoid tissue infected ex vivo with HIV-1. Productively infected CD4+ T cells were defined as CD3+ CD8− p24+, as described in the text. To evaluate CD4+-T-cell depletion, cells were mechanically isolated from control and infected matched tissues (27 pooled blocks for each variant) on day 12 postinfection, stained for CD3, CD4, CD8, and p24, and analyzed with flow cytometry. Depletion is expressed as 100% minus the percentage of CD4+ T cells that remained in the tissue after 12 days of infection, evaluated as described earlier (23, 29). Presented are average depletion values ± standard errors of the means for tissues from 4 to 12 donors. (C) Correlation between depletion and virus infection of CD4+ T cells in ex vivo-infected human lymphoid cultures. Accessory gene deletions are indicated in the following order: Vpr, Vpu, Nef.
